Effect of Extracts from Chinese Ginger, Garlic and Coriander on Removing Fishy Taste of Tilapia Fillets and Optimization of Deodorization Formula
-
摘要: 为开发一种天然来源的脱腥剂,研究姜、蒜、香菜提取液对罗非鱼片腥味的影响。以罗非鱼片为原料,通过单因素实验研究了不同浓度(2、4、6、8、10 g/L)姜、蒜、香菜提取液对罗非鱼片腥味值、脂肪氧化及菌落总数的影响,再通过响应面试验优化三种提取液的浓度。结果表明,姜、蒜、香菜提取液在浓度为6~8 g/L时能有效减轻新鲜罗非鱼片的腥味值,并抑制冷藏过程中腥味物质的产生;三种提取液对硫代巴比妥酸值的最佳抑制浓度皆为8 g/L,蒜提取液处理组的抑制效果较好;姜、蒜、香菜提取液最适的抑菌浓度为8、8、10 g/L,蒜提取液处理组的抑菌效果较好。通过响应面优化得到的三种提取液复合脱腥的配方为:姜提取液8.9 g/L、蒜提取液7.5 g/L、香菜提取液5.8 g/L,在此条件下新鲜罗非鱼片腥味值为0.42。姜、蒜、香菜提取液复配对去除罗非鱼片的腥味具有较好的效果。Abstract: With the growing demand for a natural deodorizer, ginger, garlic and coriander extracts were proposed to remove the fishy smell of tilapia fillets. The effects of different concentrations of ginger, garlic and coriander extracts on the fishy smell value, fat oxidation and total bacterial count of tilapia fillet were studied by single factor experiments. Then the proportion of the three extracts was optimized by response surface test. The results showed that ginger, garlic and coriander extracts at concentrations of 6~8 g/L could effectively reduce the fishy smell value of fresh tilapia fillets and inhibit the production of fishy smell during cold storage. All of the three extracts could significantly inhibit the increase of thiobarbital acid value at concentrations of 8 g/L and the garlic extract had better inhibition effect. Ginger, garlic and coriander extracts could effectively reduce the total bacterial count of tilapia fillets during cold storage at concentrations of 8, 8, 10 g/L respectively. The antibacterial effect of garlic extract was better than the other extracts. The optimum compound concentrations of the three extracts to remove the fishy smell were as follow: 8.9 g/L of ginger extract, 7.5 g/L of garlic extract and 5.8 g/L of coriander extract. The fishy smell value of fresh tilapia fillet was 0.42 in this optimum formula. The compound combination of ginger, garlic and coriander extracts had a better effect on removing fishy smell of tilapia fillet.
-
罗非鱼是世界主要养殖淡水鱼类,我国是罗非鱼生产大国,2020年产量达165.5万t[1],养殖产品除了鲜活销售外,还加工成鱼片、鱼罐头、烤鱼等产品。但罗非鱼有一定的腥味,降低了产品的可接受性,一直是加工中亟待解决的问题。
淡水鱼腥味的来源主要是养殖环境中水生生物、微生物及其代谢产物的吸附[2],以及自身脂肪氧化的结果[3],贮藏期间鱼肉在微生物作用下导致的品质变化也是腥味的来源之一[4]。常用的脱腥方法有物理吸附法、化学脱腥法和生物脱腥法,针对不同的腥味来源具有各自的作用优势[5]。近年来,天然产物来源的脱腥剂受到广泛关注。迷迭香、葡萄籽、鼠尾草、百里香、茶叶等提取物对鱼类腥味的抑制都有相关的研究。黄丕苗等[6]研究发现迷迭香提取物能去除白鲢主要腥味物质;Guan等[7]研究了葡萄籽、鼠尾草对冷藏带鱼鱼丸的腥味等挥发性成分有明显的抑制作用;Khalafalla等[8]发现百里香提取物和迷迭香提取物可提高冷藏罗非鱼的感官特性;刘方芳等[9]发现利用红茶处理胭脂鱼能减弱腥味、改善风味。采用天然来源的调料和香料掩盖鱼腥味,具有脱腥效果好、成本低、食用安全的特点,吴燕燕等[10]报道了香菜和香茅可有效脱除鲜鲈鱼鱼片腥味。但如何将天然物质用于水产品加工中的腥味脱除,以及天然物质对罗非鱼片的脱腥作用尚少有报道。
本文采用姜、蒜、香菜对罗非鱼片进行脱腥处理,研究三种提取液浸泡对罗非鱼片腥味值、硫代巴比妥酸值及菌落总数的影响,得到三种提取液的复合脱腥配方,为罗非鱼产品加工提供研究基础,对提高罗非鱼加工率具有重要意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与设备
鲜活罗非鱼(600±50 g)、新鲜姜、蒜、香菜 广州市华润万家超市;PCA营养琼脂 广东环凯生物科技有限公司;2-硫代巴比妥酸、三氯乙酸、氯仿 分析纯,广州化学试剂厂。
LDZX-75KBS型立式压力蒸汽灭菌器 上海申安医疗器械厂;SPX型智能生化培养箱 宁波江南仪器厂;DZ500/2D真空包装机 温州新泰包装机械厂;D-78224超声波清洗仪 德国艾尔玛公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 姜、大蒜、香菜提取液的制备
根据Cao等[11]的方法略作修改。将姜、蒜、香菜等材料清洗干净,沥干,各称取100 g与200 mL蒸馏水混合均匀,匀浆,定容至500 mL,40 ℃超声处理30 min(200 W,40 kHz),真空抽滤后将滤液定容至1 L,得到质量浓度为100 g/L的提取液原液。原液按比例稀释后可配制成质量浓度为10、8、6、4、2 g/L的稀释液。
1.2.2 单因素实验
罗非鱼敲击致死后,每条鱼取两片鱼片(约20 cm×11 cm),分别用不同浓度的姜、蒜、香菜提取液(0、2、4、6、8、10 g/L)以料液比1:3(w:w)浸泡25 min,取出沥干后真空包装。以感官评定、硫代巴比妥酸值和菌落总数为指标测定腥味变化、脂肪氧化情况和微生物生长情况,以0 g/L的样品组为空白组,分别于浸泡包装后(0 d,新鲜浸泡鱼片)和4 ℃贮藏后(5 d,贮藏鱼片)测定。
1.2.3 响应面优化试验
综合单因素实验结果,根据Box-Behnken设计原理,以姜、蒜、香菜提取液的浓度为自变量,以鱼片浸泡后的感官评定的腥味值为响应值设计实验,研究各自变量及其交互作用对罗非鱼片的脱腥效果,优化脱腥配方。利用Design Expert 12.0对结果进行回归拟合及方差分析,因素水平设计如表1所示。
表 1 响应面试验因素及水平Table 1. Factors and levels for response surface test水平 因素 A姜提取液(g/L) B蒜提取液(g/L) C香菜提取液(g/L) −1 6 4 4 0 8 6 6 1 10 8 8 1.2.4 感官评价
参考赵萍等[3]的方法,略作修改。将样品于100 ℃条件下蒸5 min,放入白瓷盘中。感官评定人员剪开包装袋后通过气味及品尝样品进行评分,以腥味值为主要指标。感官评价人员由10名经过专业培训的人员组成,评价过程独立完成。感官评分标准见 表2,腥味值的范围0~5分,分值越低,说明脱腥效果越好。
表 2 感官评分标准Table 2. Scoring stand of sensory test腥味值 无腥味 腥味很淡 腥味淡 腥味明显 腥味较浓 腥味浓 评分 0 1 2 3 4 5 1.2.5 硫代巴比妥酸值(Thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances,TBARS)测定
根据Yarnpakdee等[12]的方法测定,略作修改。将5 g鱼肉切碎,与25 mL硫代巴比妥酸溶液(0.375 g/L硫代巴比妥酸,15 g/L三氯乙酸,0.25 mol/L HCl)4 ℃下均质30 s,4 ℃下振荡30 min,沸水浴10 min,冷却后4 ℃下3600 r/min离心20 min,取上清液,于532 nm处测量吸光度。以浓度为0至6 mg/L的1,1,3,3-四甲氧基丙烷为标准溶液测量吸光度后绘制标准曲线,标准曲线方程为y=0.4158x−0.0081(R2=0.9997),结果以丙二醛((Malondialdehyde,MDA)含量来表示。
1.2.6 菌落总数的测定
参照GB 4789.2-2016《食品微生物学检验菌落总数测定》。
1.3 数据处理
采用Excel软件进行数据处理、显著性分析及作图,Design Expert 12.0软件进行响应面分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 姜、蒜、香菜提取液对罗非鱼片感官评价的影响
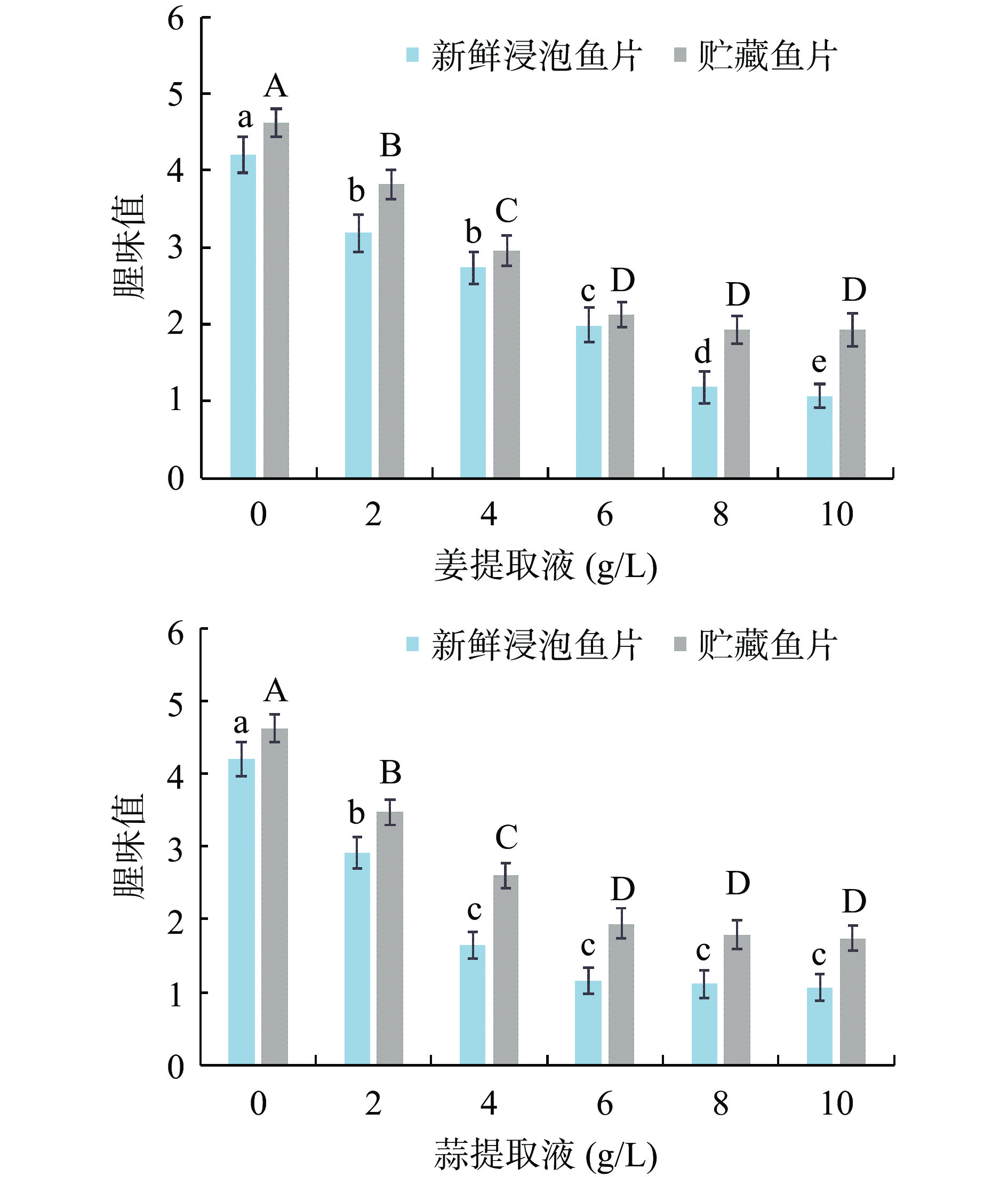
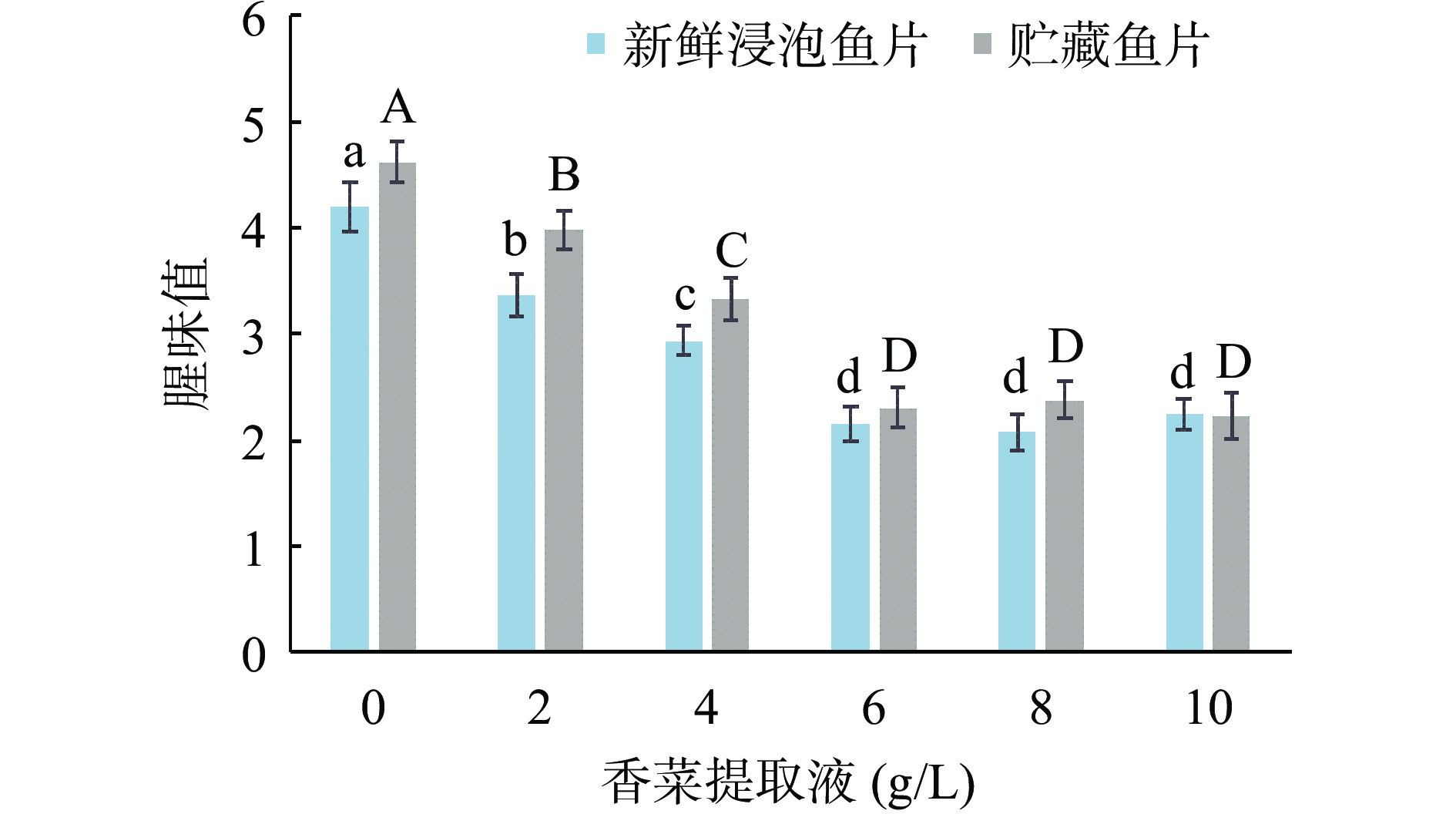
由图1可知,新鲜罗非鱼片经姜、蒜、香菜提取液处理后,腥味均得到显著改善(P<0.05)。经不同浓度姜、蒜、香菜提取液处理的罗非鱼片在浸泡后和4 ℃贮藏5 d后,相较于未处理的罗非鱼片(0 g/L),腥味值显著降低(P<0.05)。相对于浸泡后即时感官评定的罗非鱼片,4 ℃贮藏5 d后的罗非鱼片中整体的腥味可接受度略低,这是由于鱼肉贮藏过程中因生化反应和微生物作用产生不愉快气味。在每种提取液处理的鱼片中,腥味值随处理浓度的增加而降低,因此适当提升提取液的浓度有助于提高对罗非鱼腥味的掩盖作用,但是过高的浓度会带入明显的提取液本身的风味,导致产品可接受度下降。因此,姜、蒜、香菜在处理浓度为6~8 g/L时腥味值较低,感官评价较好。姜、蒜、香菜提取液的去腥主要是通过浸泡等工艺处理鱼体,利用特有的风味成分掩盖鱼体腥味,如大蒜中的蒜氨酸、生姜中的姜精油和姜辣素等[13]。姜、葱、蒜等香辛料在大西洋鲭鱼[14]、白鲢鱼[15]、草鱼[16]、小黄鱼[17]等水产品的脱腥中也有应用,对腥味的掩盖效果较好且被广泛应用。
2.2 姜、蒜、香菜提取液对罗非鱼鱼片硫代巴比妥酸值的影响
脂肪氧化是鱼肉产生腥味的主要原因之一[18]。丙二醛是鱼肉中的多不饱和脂肪酸氧化产生的代谢产物,是评估脂肪氧化程度的常用指标,也是评估鱼肉气味恶化的重要指标[19]。由图2可知,在新鲜浸泡罗非鱼片中,三种提取液对TBARS的影响均无显著性差异(P>0.05)。罗非鱼片冷藏5 d后,对照组(0 g/L组)的TBARS从0.091 g/kg增加到0.323 g/kg,而经姜、蒜、香菜提取液处理的罗非鱼片的TBARS增幅明显放缓,其中蒜提取液处理组的抑制效果最好,香菜提取液处理组效果最差。姜、蒜、香菜提取液的最佳抑制浓度皆为8 g/L。据报道,姜中的多酚化合物(6-姜酚及衍生物)可抑制鸭肉中脂肪氧化物质的产生[20];大蒜中的有机硫化物可显著延缓牛肉中氧合肌红蛋白和脂质的氧化[21];香菜水提液具有还原活性,可螯合铁离子,清除自由基等,从而抑制脂质氧化[22],本实验结果与上述文献相似。
2.3 姜、蒜、香菜提取液对罗非鱼片菌落总数的影响
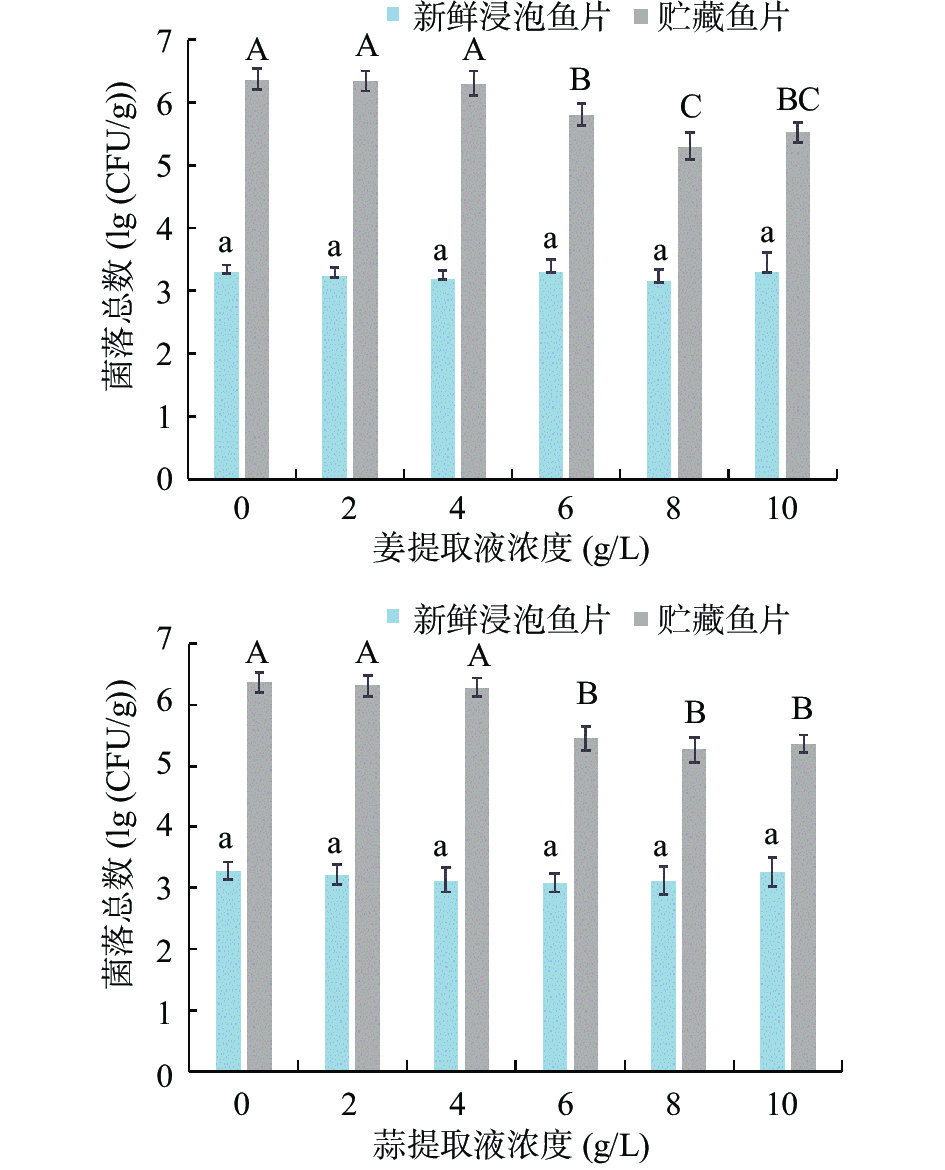
由图3可知,与对照组(0 g/L)比,新鲜罗非鱼片在姜、蒜、香菜提取液处理后,菌落总数并无明显变化(P>0.05)。但罗非鱼片在4 ℃冷藏5 d后,处理组中的较高浓度(8~10 g/L)的大蒜提取液可以显著抑制微生物的生长(P<0.05)。姜、蒜、香菜提取液最适的抑菌浓度为8、8、10 g/L,蒜提取液的抑菌效果最好,香菜提取液的抑菌效果最差。Sivasothy等[23]报道姜中的山奈酚、姜黄素等不仅具有抗氧化性,还具有抑菌作用。蒜水提物对肉制品中主要食源性病原体(大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌)生长具有有效的抑制作用[24]。
2.4 响应面法优化姜、蒜、香菜提取液对罗非鱼片的脱腥配方
2.4.1 响应面优化结果
采用Box-Behnken实验设计方法,在单因素实验的基础上,选择姜、蒜、香菜的提取液浓度为自变量,腥味值为响应值,对鱼片浸泡姜、蒜、香菜提取液后进行感官评定,实验结果见表3。
表 3 响应面试验设计及结果Table 3. Design and results of response surface experiment实验号 A姜提取液
(g/L)B蒜提取液
(g/L)C香菜提取液
(g/L)Y腥味值 1 −1 −1 0 1.494 2 1 −1 0 1.159 3 −1 1 0 0.642 4 1 1 0 0.461 5 −1 0 −1 1.037 6 1 0 −1 0.829 7 −1 0 1 0.948 8 1 0 1 0.713 9 0 −1 −1 1.328 10 0 1 −1 0.597 11 0 −1 1 1.267 12 0 1 1 0.535 13 0 0 0 0.573 14 0 0 0 0.561 15 0 0 0 0.566 16 0 0 0 0.558 17 0 0 0 0.579 2.4.2 响应面模型建立及方差分析
采用Design Expert 12.0软件对响应面实验结果进行回归拟合及方差分析,得到二次回归拟合方程为:Y=0.5674−0.119875A−0.376625B−0.041C+0.0385AB−0.00675AC−0.00025BC+0.1608A2+0.2108B2+0.15355C2
对响应面回归模型进行方差分析和显著性检验,如表4所示。
表 4 回归模型的方差分析结果Table 4. Analysis of variance results of the regression model方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F P 显著性 回归模型 1.71 9 0.1900 483.55 <0.0001 ** A-姜提取液 0.1150 1 0.1150 292.63 <0.0001 ** B-蒜提取液 1.13 1 1.13 2888.56 <0.0001 ** C-香菜提取液 0.0134 1 0.0134 34.23 0.0006 ** AB 0.0059 1 0.0059 15.09 0.0060 ** AC 0.0002 1 0.0002 0.4639 0.5177 BC 2.5×10−7 1 2.5×10−7 0.0006 0.9806 A² 0.1089 1 0.1089 277.13 <0.0001 ** B² 0.1871 1 0.1871 476.27 <0.0001 ** C² 0.0993 1 0.0993 252.70 <0.0001 ** 残差 0.0027 7 0.0004 失拟项 0.0025 3 0.0008 0.6392 0.7425 纯误差 0.0003 4 0.0001 总和 1.71 16 R2=0.9984 R2adj=0.9963 注:**表示差异极显著,P<0.01。 由表4可以看出,回归模型P<0.0001,模型差异显著,失拟项P>0.05,差异不显著,说明该模型拟合较好,能够描述各因素与响应值的关系。模型中的决定系数R2=0.9984>0.95,调整决定系数R2adj=0.9963>0.95,表明试验结果与模型之间拟合度较高。由模型中因子A、B、C、交互项AB和二次项A²、B²、C²的P值可以看出,其对响应值的影响均为极显著水平(P<0.01);由表中F值可知,各因素对罗非鱼片腥味值的影响程度依次是:蒜提取液(B)>姜提取液(A)>香菜提取液(C)。
2.4.3 响应面交互作用分析
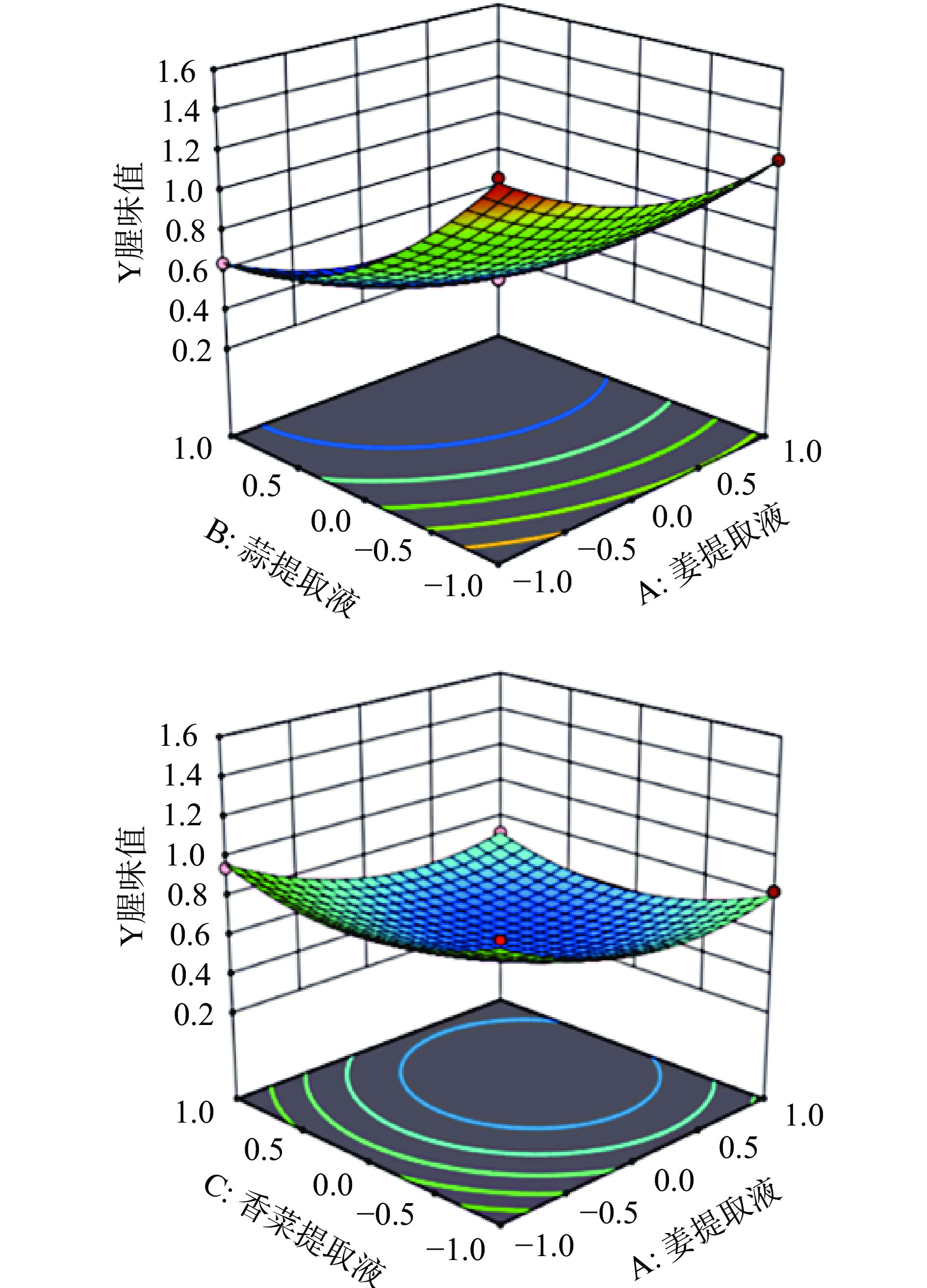
响应面的弯曲程度反映了各因素对响应值的影响大小,曲面图中曲线的弯曲程度越大,说明相应的因素对响应值的影响越显著[25]。等高线图用于反映两个因素之间交互作用的大小,两个因素交互作用显著时等高线为椭圆形,交互作用较弱时等高线趋于圆形[26]。由图4可以看出,姜提取液与蒜提取液交互作用对罗非鱼腥味值的影响显著。当蒜提取液的浓度固定不变时,随着姜提取液添加量的增加鱼片腥味值逐渐减小,在9 g/L左右达到最低值,之后随着浓度的增大腥度值变化不大,说明浓度在9 g/L以上对腥味值的变化影响不大。
2.4.4 模型优化及验证
根据软件对三种脱腥剂优化的预测结果,结合实际情况,最终确定三种提取液的浓度为:姜提取液8.9 g/L、蒜提取液7.5 g/L、香菜提取液5.8 g/L,在此条件下新鲜浸泡罗非鱼片腥味值的预测值为0.40。在此优化条件下进行了三次验证试验,实际得到的罗非鱼片腥味值为0.42±0.08,验证结果与理论预测值相接近,说明该响应面模型与实际情况的拟合较好。
3. 结论
新鲜罗非鱼片经姜、蒜、香菜提取液处理后,腥味均有得到显著的改善,冷藏5 d后,相对于与未处理的罗非鱼肉,腥味显著降低(P<0.05)。三种提取液(8~10 g/L)处理罗非鱼片后能显著抑制TBARS及菌落总数的增长(P<0.05),从而减少腥味物质的产生。通过响应面优化得到的三种提取液复合脱腥的配方为:姜提取液8.9 g/L、蒜提取液7.5 g/L、香菜提取液5.8 g/L。在此条件下新鲜浸泡罗非鱼片腥味值为0.42,能明显消除罗非鱼片的腥味,使用该优化配方处理罗非鱼片能抑制腥味物质的产生,在一定程度上提升产品品质。
-
表 1 响应面试验因素及水平
Table 1 Factors and levels for response surface test
水平 因素 A姜提取液(g/L) B蒜提取液(g/L) C香菜提取液(g/L) −1 6 4 4 0 8 6 6 1 10 8 8 表 2 感官评分标准
Table 2 Scoring stand of sensory test
腥味值 无腥味 腥味很淡 腥味淡 腥味明显 腥味较浓 腥味浓 评分 0 1 2 3 4 5 表 3 响应面试验设计及结果
Table 3 Design and results of response surface experiment
实验号 A姜提取液
(g/L)B蒜提取液
(g/L)C香菜提取液
(g/L)Y腥味值 1 −1 −1 0 1.494 2 1 −1 0 1.159 3 −1 1 0 0.642 4 1 1 0 0.461 5 −1 0 −1 1.037 6 1 0 −1 0.829 7 −1 0 1 0.948 8 1 0 1 0.713 9 0 −1 −1 1.328 10 0 1 −1 0.597 11 0 −1 1 1.267 12 0 1 1 0.535 13 0 0 0 0.573 14 0 0 0 0.561 15 0 0 0 0.566 16 0 0 0 0.558 17 0 0 0 0.579 表 4 回归模型的方差分析结果
Table 4 Analysis of variance results of the regression model
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F P 显著性 回归模型 1.71 9 0.1900 483.55 <0.0001 ** A-姜提取液 0.1150 1 0.1150 292.63 <0.0001 ** B-蒜提取液 1.13 1 1.13 2888.56 <0.0001 ** C-香菜提取液 0.0134 1 0.0134 34.23 0.0006 ** AB 0.0059 1 0.0059 15.09 0.0060 ** AC 0.0002 1 0.0002 0.4639 0.5177 BC 2.5×10−7 1 2.5×10−7 0.0006 0.9806 A² 0.1089 1 0.1089 277.13 <0.0001 ** B² 0.1871 1 0.1871 476.27 <0.0001 ** C² 0.0993 1 0.0993 252.70 <0.0001 ** 残差 0.0027 7 0.0004 失拟项 0.0025 3 0.0008 0.6392 0.7425 纯误差 0.0003 4 0.0001 总和 1.71 16 R2=0.9984 R2adj=0.9963 注:**表示差异极显著,P<0.01。 -
[1] 农业部渔业渔政管理局. 中国渔业统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2021: 24−25. Fisheries and Fisheries Administration of the Ministry of Agriculture. China fisheries statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House, 2021: 24−25
[2] 吴静, 黄卉, 李来好, 等. 鱼制品腥味产生机制及调控措施研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(24):254−261. [WU J, HUANG H, LI L H, et al. Review on the formation and regulation of the fishy odor in fish products[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(24):254−261. WU J, HUANG H, LI L H, et al. Review on the formation and regulation of the fishy odor in fish products[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2019, 45(24): 254-261.
[3] 赵萍, 陈小华, 刘俊霞, 等. 生姜/料酒脱腥过程中大鲵肝挥发性有机物动态变化[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(24):164−172. [ZHAO P, CHEN X H, LIU J X, et al. Dynamic changes of volatile organic compounds in giant salamander (Andrias davidiauns) liver during ginger /cooking wine deodorization[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(24):164−172. ZHAO P, CHEN X H, LIU J X, et al. Dynamic changes of volatile organic compounds in giant salamander (Andrias davidiauns) liver during ginger /cooking wine deodorization[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(24) (24): 164-172.
[4] HOWGATE P. Tainting of farmed fish by geosmin and 2-methyl-iso-borneol: A review of sensory aspects and of uptake/depuration[J]. Aquaculture,2004,234(1):155−181.
[5] 卢祺, 刘津延, 刘方芳, 等. 鱼类腥味物质及脱腥技术研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(8):285−291. [LU Q, LIU J Y, LIU F F, et al. Research progress on fishy smell and technology of removing off-odor[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(8):285−291. LU Q, LIU J Y, LIU F F, et al. Research progress on fishy smell and technology of removing off-odor[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(8): 285-291.
[6] 黄丕苗, 王智荣, 陈湑慧, 等. 迷迭香提取物对白鲢鱼肉腥味的影响及其脱腥条件优化[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(6):176−183. [HUANG P M, WANG Z R, CHEN X H, et al. Effect of rosemary extract on the fishy odour of silver carp and the optimization of deodorizing conditions[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(6):176−183. HUANG P M, WANG Z R, CHEN X H, et al. Effect of rosemary extract on the fishy odour of silver carp and the optimization of deodorizing conditions[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(6): 176-183.
[7] GUAN W, REN X, LI Y, et al. The beneficial effects of grape seed, sage and oregano extracts on the quality and volatile flavor component of hairtail fish balls during cold storage at 4 ℃[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2019,101:25−31. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.11.024
[8] KHALAFALLA F A, ALI F H M, HASSAN A R H A. Quality improvement and shelf-life extension of refrigerated Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fillets using natural herbs[J]. Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences,2015,4(1):33−40. doi: 10.1016/j.bjbas.2015.02.005
[9] 刘方芳, 卢祺, 刘津延, 等. 响应面优化美国大口胭脂鱼脱腥条件[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(18):167−172. [LIU F F, LU Q, LIU J Y, et al. Optimization of deodorization conditions of American bigmouth bass using response surface[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(18):167−172. LIU F F, LU Q, LIU J Y, et al. Optimization of deodorization conditions of American bigmouth bass using response surface[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(18): 167-172.
[10] 吴燕燕, 朱小静, 林婉玲, 等. 香菜和香茅对鲜鲈鱼片的脱腥、抑菌效果[J]. 中国食品学报,2018,18(12):188−194. [Wu Y Y, Zhu X J, Lin W L, et al. Effect of Chinese parsley (Coriandrum sativum) and citronella (Moslachinensis Maxim) on removing fishy taste and bacteriostasis of fresh Micropterus salmoides fillets[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2018,18(12):188−194. Wu Y Y, Zhu X J, Lin W L, et al. Effect of Chinese parsley (Coriandrum sativum) and citronella (Moslachinensis Maxim) on removing fishy taste and bacteriostasis of fresh Micropterus salmoides fillets[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2018, 18(12): 188-194.
[11] CAO Y, GU W, ZHANG J, et al. Effects of chitosan, aqueous extract of ginger, onion and garlic on quality and shelf life of stewed-pork during refrigerated storage[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,141(3):1655−1660. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.04.084
[12] YARNPAKDEE S, BENJAKUL S, NALINANON S, et al. Lipid oxidation and fishy odour development in protein hydrolysate from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) muscle as affected by freshness and antioxidants[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,132(4):1781−1788. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.11.139
[13] 胡苑, 施文正, 卢瑛. 鱼类腥味脱除技术研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(5):282−287. [HU Y, SHI W Z, LU Y. Recent advances on deodorization technology of fishy odors[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(5):282−287. HU Y, SHI W Z, LU Y. Recent advances on deodorization technology of fishy odors[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(5): 282-287.
[14] 吴吉玲, 黄一珍, 姜鹏飞, 等. 排序法在大西洋鲭鱼脱腥工艺筛选中的应用[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(23):73−79. [WU J L, HUANG Y Z, JIANG P F, et al. Application of ranking test in screening of Atlantic Mackerel (Scomber scombrus) deodorization process[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(23):73−79. WU J L, HUANG Y Z, JIANG P F, et al. Application of ranking test in screening of Atlantic Mackerel(Scomber scombrus) deodorization process[J]. Food Research and Development, 2020, 41(23): 73-79.
[15] 廖涛, 杨玉平, 白婵, 等. 白鲢鱼体内腥味物质的脱除方法研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(21):49−58. [LIAO T, YANG Y P, BAI C, et al. Study on removal technologies of off-odor in silver carp[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(21):49−58. LIAO T, YANG Y P, BAI C, et al. Study on removal technologies of off-odor in silver carp[J]. Food Research and Development, , 2018, 39(21): 49-58.
[16] 周若琳, 胡盛本, 姚磊, 等. 草鱼不同部位挥发性成分分析及生姜脱除草鱼腥味物质的工艺研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(20):177−182. [ZHOU R L, HU S B, YAO L, et al. Volatiles from different parts of grass carp and the process of ginger in removing fishy smell[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(20):177−182. ZHOU R L, HU S B, YAO L, et al. Volatiles from different parts of grass carp and the process of ginger in removing fishy smell[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2017, 38(20): 177-182.
[17] 沈艳奇. 低温真空油炸小黄鱼调理食品的研制[D]. 锦州: 渤海大学, 2019 Research on a ready-to-eat food for low-temperature vacuum fried small yellow croaker processing technology[D]. Jinzhou: Bohai University, 2019.
[18] YARNPAKDEE S, BENJAKUL S, KRISTINSSON H G. Lipid oxidation and fishy odour in protein hydrolysate derived from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) protein isolate as influenced by haemoglobin[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2014,94(2):219−226. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6235
[19] PAPASTERGIADIS A, MUBIRU E, LANGENHOVE V H, et al. Malondialdehyde measurement in oxidized foods: evaluation of the spectrophotometric thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) test in various foods[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2012,60(38):9589−9594. doi: 10.1021/jf302451c
[20] SURYANTI U, BINTORO V P, ATMOMARSONO U, et al. Antioxidant activity of Indonesian endogenous duck meat marinated in ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) extract[J]. International Journal of Poultry Science,2014,13(2):102. doi: 10.3923/ijps.2014.102.107
[21] YIN M, CHENG W. Antioxidant and antimicrobial effects of four garlic-derived organosulfur compounds in ground beef[J]. Meat Science,2003,63(1):23−28. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1740(02)00047-5
[22] WONG P Y Y, KITTS D D. Studies on the dual antioxidant and antibacterial properties of parsley (Petroselinum crispum) and cilantro (Coriandrum sativum) extracts[J]. Food Chemistry,2006,97(3):505−515. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.05.031
[23] SIVASOTHY Y, SULAIMAN S F, OOI K L, et al. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of flavonoids and curcuminoids from Zingiber spectabile Griff[J]. Food Control,2013,30(2):714−720. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.09.012
[24] ROSE P, WHITEMAN M, MOORE P K, et al. Bioactive S–alk (en) yl cysteine sulfoxide metabolites in the genus Allium: the chemistry of potential therapeutic agents[J]. Natural Product Reports,2005,22(3):351−368. doi: 10.1039/b417639c
[25] 井月欣, 乔瑞光, 张健, 等. 响应面试验优化盐渍仿刺参脱盐工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(18):160−164. [JING Y X, QIAO R G, ZHANG J, et al. Optimization of desalting process of salted Apostichopus japonicus by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(18):160−164. JING Y X, QIAO R G, ZHANG J, et al. Optimization of desalting process of salted Apostichopus japonicus by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2017, 38(18): 160-164.
[26] 陶文斌, 吴燕燕, 李春生, 等. 响应面法优化腌制大黄鱼的低钠复合咸味剂配方[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(19):136−144. [TAO W B, WU Y Y, LI C S, et al. Optimization of low-sodium compound salty agent formula for pickled Larimichthys crocea fillets by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(19):136−144. TAO W B, WU Y Y, LI C S, et al. Optimization of low-sodium compound salty agent formula for pickled Larimichthys crocea fillets by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(19): 136-144.





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
