Chemical Components of Swim Bladder and Donkey Skin and Their Improvement Effects on Cyclophosphamide-induced Anemia Mice
-
摘要: 目的:研究鱼鳔、驴皮化学成分及对环磷酰胺所致贫血小鼠的改善作用。方法:测定总蛋白含量、氨基酸组成及分子量范围;胃蛋白酶辅助提取获得胶原蛋白,并分析其含量、组成及结构;腹腔注射环磷酰胺(80 mg/kg)建立小鼠贫血模型,灌胃给予受试物(鱼鳔胶1.52 g/(kg·d)、驴皮胶1.39 g/(kg·d)),观察对脏器系数和血液学指标的影响。结果:鱼鳔、驴皮总蛋白含量均大于97%,鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶分子量在50 Da~328 kDa之间;鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白均为Ⅰ型胶原蛋白,鱼鳔胶原蛋白含量约为驴皮的6.51倍,但胶原蛋白三螺旋结构不同,鱼鳔胶原蛋白以α-螺旋结构为主,驴皮胶原蛋白以反平行为主。功效评价结果表明,给药28 d,鱼鳔胶与驴皮胶均可促进环磷酰胺贫血小鼠造血机能的恢复,以鱼鳔胶效果更佳。与模型组相比,鱼鳔胶给药组红细胞、血红蛋白、血小板、网织红细胞、脾脏及胸腺系数均得到显著改善(P<0.05);驴皮胶给药组红细胞、血红蛋白及胸腺系数显著改善(P<0.05)。结论:对鱼鳔、驴皮化学成分进行系统研究,确定了化学成分间的差异;发现鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶均可促进环磷酰胺贫血小鼠造血机能的恢复,且鱼鳔胶效果更佳,推测二者补血活性可能与氨基酸、胶原蛋白等成分有关。本研究为鱼鳔资源精深加工奠定理论基础。Abstract: Objective: To systematic study for different chemical components of swim bladder and donkey skin, and their improvement effects on cyclophosphamide-induced anemia mice. Methods: The chemical characterizations, including total protein content, amino acid composition and molecular weight were measured, respectively. Pepsin-soluble collagens were extracted from swim bladder and donkey skin by hydrochloric acid-pepsin method, and analyzed the content, composition and structure. The anemia model was established by intraperitoneal injected with cyclophosphamide at a dosage of 80 mg/kg. The coefficient of visceral organs and the hematological indexes were observed in mice with swim bladder glue (1.52 g/(kg·d)) or donkey skin glue (1.39 g/(kg·d)) by gavage administration per day. Results: The total protein contents of swim bladder and donkey skin reached more than 97%. The molecular weights of swim bladder glue and donkey skin glue ranged from 50 Da to 328 kDa. Swim bladder collagen and donkey skin collagen were both type Ⅰ collagen. While the content of collagen in swim bladder was 6.51 times than that in donkey skin. However the collagen triple helix structures were different. The swim bladder collagen had an α-helix structure, and the donkey skin collagen structure was mainly anti-parallel. After 28 days of administration, both swim bladder glue and donkey skin glue could promote the recovery of hematopoietic function in cyclophosphamide-induced anemia mice, and swim bladder glue exhibited a better effect. Compared with the model, the erythrocyte, hemoglobin, platelet, reticulocyte, spleen and thymus coefficients of the swim bladder glue were significantly improved (P<0.05). The erythrocyte, hemoglobin and thymus coefficients of the donkey skin glue were significantly improved (P<0.05). Conclusion: A systematic study of the chemical characteristics of swim bladder and donkey skin were carried out to determine the differences between the components. Pharmacodynamical research showed that swim bladder glue and donkey skin glue could promote the recovery of hematopoietic function in cyclophosphamide model mice, and the effect of swim bladder glue was better. It was hypothesized that the blood replenishing activity of the two might be related to the amino acids, collagen and other components. This work could provide a theoretical foundation for the development of swim bladder.
-
Keywords:
- swim bladder /
- donkey skin /
- chemical composition /
- cyclophosphamide /
- anemia /
- organ coefficient /
- hematology index
-
贫血是临床中常见的疾病之一,患者通常表现为头晕、乏力、困倦、面色苍白,由于贫血发病周期长,发展缓慢,常常不为人们察觉,这种疾病影响着世界上四分之一以上的人口并且发病人群广[1],对人们的生活质量造成一定的影响。在中医学中贫血属于“血虚”“血枯”的范畴,多与气血不足,脏腑失养相关[2],自古针对补血药材多有记载,其中不乏各种动物胶类如驴皮胶、牛皮胶、龟甲胶等[3−4],深受人们喜爱。
我国是海洋大国,海洋生物资源丰富,随着近年对海洋资源的开发愈加重视,许多海产品受到消费者的关注,其中海洋胶类逐渐进入大家的视野。鱼鳔药用历史悠久,味甘、咸,性平,归肾、肝、脾、胃经,具有滋补肝肾,补精益阳,补气养血,活血止血,解毒敛疮等功效[5],其与燕窝、鱼翅齐名,为“海洋八珍之一”,素有“海洋人参”之美誉,是一味海洋滋补上品[6−7]。鱼鳔不仅含有丰富的蛋白质、少量的脂肪和糖类物质,还含有丰富的无机元素、维生素等[8−10]。目前,已上市的鱼鳔产品如鱼鳔补肾丸、固本延龄丸等中成药,多以补肾固精功效为主。当前鱼鳔主流产品为药用典籍中记载的黄鱼鳔,及非药用典籍的鳘鱼鳔和鳕鱼鳔,前期课题组比较了上述3种鱼鳔提取制备的鱼鳔胶对环磷酰胺所致贫血小鼠的改善作用,发现三种基原的鱼鳔胶对环磷酰胺所致贫血小鼠的红细胞、血红蛋白、血小板、网织红细胞等血液学指标及胸腺、脾脏系数均有不同程度的改善作用,其中鳘鱼鳔胶改善效果最佳。
作为海洋胶类代表的鱼鳔,现多是对其营养价值的研究,尚未有关鱼鳔系统的化学成分及药效物质基础的研究。因此,本文对鳘鱼鳔的总蛋白、氨基酸组成及胶原蛋白等化学成分进行了研究,评价了其对贫血小鼠的血液学指标及脏器系数的改善作用,并与陆地代表胶类驴皮胶进行比较。通过本文研究,以期为后续阐明鱼鳔药效物质基础及开发具有海洋特色的鱼鳔补血类产品奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
鳘鱼鳔 产地山东省青岛市;驴皮 产地山东省聊城市;胃蛋白酶(酶活力≥400 U/mg)、浓缩胶(5%)、分离胶(8%) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;人I型胶原蛋白(COLI)ELISA试剂盒 美国Peprotech公司;氨基酸混合标准品 和光纯药工业株式会社;溴化钾(KBr) 光谱纯,Sigma公司;葡聚糖系列标准品(相对分子质量分别为180、2700、5250 、9750、13050、36800、64650、135350 Da) 中国食品药品检定研究院;环磷酰胺 江苏恒瑞医药股份有限公司;无水乙醇、硫酸、硫酸铜、硫酸钾、硼酸、甲基红、溴甲酚绿、盐酸、氯化钠、氢氧化钠、三氯乙酸、乙二胺四乙酸二钠(EDTA)、冰醋酸、考马斯亮蓝、甲醇、柠檬酸钠 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;RBC、HGB、PLT、RET血液学测试试剂包 济南希森美康医用电子有限公司;SPF级昆明小鼠 济南朋悦实验动物繁育有限公司,40只,体重18~22 g,雄性,生产许可证号:SCXK(鲁)2019-0003。
K9840凯氏定氮仪 济南海能仪器股份有限公司;MS 105DU型电子天平 上海梅特勒-托利多公司;SCIENTZ-18N冻干机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;LA8080型氨基酸自动分析仪 日本株式会社日立高新技术科技;FA-1004电子天平 上海舜宇恒平科学仪器有限公司;BR4I型离心机、Nicolet iS5傅里叶红外变换光谱仪 美国Thermo Fisher Scientific;UV-6000PC紫外分光光度计 上海元析仪器有限公司;DF-68 15T型粉末压片机 武汉鼎福汇聚科技有限公司;Chirascan q CD圆二色谱仪 英国Applied PhotoPhysics公司;Aglient 1260 Ⅱ型高效液相色谱仪 美国安捷伦科技有限公司;VORTEX GENIUS型涡旋混合器 德国IKA公司;H1650-W型台式高速离心机 湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 鱼鳔、驴皮总蛋白分析
参照GB 5009.5-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中蛋白质的测定》第一法凯氏定氮法[11]测定鱼鳔、驴皮中总蛋白含量。
1.2.2 鱼鳔、驴皮氨基酸组成分析
参照GB 5009.124-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中氨基酸的测定》方法[12]分别对鱼鳔、驴皮的氨基酸组成进行分析。
1.2.3 鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶分子量分析
1.2.3.1 鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶提取制备
分别称取适量鱼鳔、驴皮,剪成小块,加30倍量水回流提取4 d,提取液4000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液,减压浓缩后冷冻干燥,获得鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶干膏。
1.2.3.2 鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶分子量分布考察
采用凝胶色谱法[13]测定鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶分子量范围:分别称取系列葡聚糖标准品、鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶干膏适量,精密称定,加0.1 mol/L的Na2SO4溶液溶解,配制成5 mg/mL的溶液,用0.22 µm水相微孔滤膜过滤,得对照品溶液及鱼鳔胶和驴皮胶供试品溶液。精密吸取上述对照品溶液及供试品溶液各20 µL液相分析,采用TSKgel GMPWXL(4.6×250 mm,5 μm)色谱柱,以0.1 mol/L的Na2SO4溶液为流动相,流速0.5 mL/min,柱温35 ℃,示差检测器(RID)检测。以保留时间为横坐标(X),分子量对数为纵坐标(Y)绘制标准曲线,得回归方程:Y=−0.51X+12.95,R2=0.9937,计算鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶峰位分子量及分子量分布。
1.2.4 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白分析
1.2.4.1 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白提取制备
参考文献[14]的方法分别称取鱼鳔、驴皮各20 g,剪碎加蒸馏水泡发,按质量比1:30加入预冷的0.1 mol/L NaOH处理48 h,用来去除非胶原成分,再用冰水冲洗至中性。加入30倍体积预冷的pH7.4的0.5 mol/L EDTA处理48 h,用来去除矿物质,用冰水冲洗至中性;25000 r/min匀浆10 min后,将其混悬于150倍体积含0.1 g/100 mL胃蛋白酶的0.5 mol/L冰醋酸中,搅拌提取48 h。提取液10000 r/min离心30 min,上清液迅速用6 mol/L NaOH调节pH7.5,边搅拌边向其缓慢加入磨细的NaCl粉末,至NaCl终浓度为2.6 mol/L,待NaCl全部溶解,静置过夜,10000 r/min离心30 min,沉淀加适量0.5 mol/L的冰醋酸复溶,10000 r/min离心30 min,取上清液透析(MD31:0.1~0.5 kDa)除盐,先用0.1 mol/L的冰醋酸透析过夜,换去离子水透析72 h,期间换水数次,获得的透析液转至冻干盘,冷冻干燥,分别获得鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白。
1.2.4.2 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白含量测定
采用人I型胶原蛋白(COLI)ELISA试剂盒测定鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白含量。称取鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白配制成质量浓度10 mg/mL的胶原溶液,上样前稀释100倍。收集细胞培养液的上清液进行COLI的ELISA检测,将阴性对照组及待检测样品(每个样品各3组平行)加入96孔板,每孔100 μL。绘制标准曲线并在450 nm波长下观察标准品及鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白样品的吸光度,计算Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的浓度。
1.2.4.3 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白氨基酸组成分析
同1.2.2。
1.2.4.4 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白SDS-PAGE电泳
参考Laemmli[15]的方法,分别称取鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白适量,精密称定,加0.5 mol/L乙酸溶解,配制成质量浓度为1 mg/mL的胶原溶液,用6 mol/L NaOH中和至pH7.0,10000 r/min 4 ℃离心30 min,取30 μL上清液,加10 μL 4%上样缓冲液(含β-巯基乙醇),混匀后,煮沸5 min,冷却后再次离心,取10 μL上样进行SDS-PAGE电泳。聚丙烯酰胺凝胶由5%浓缩胶(pH6.8),8%分离胶(pH8.8)组成。电泳结束后将胶条置于三氯乙酸溶液中固定15 min,染色1 h(染色液为0.1%考马斯亮蓝R-250-甲醇-冰醋酸,体积比9:9:2),随后脱色(脱色液为冰醋酸-甲醇-水,体积比1:1:8)至胶条上的条带清晰可见即可。
1.2.4.5 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白紫外全波长扫描分析
分别称取鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白适量,精密称定,加0.5 mol/L乙酸溶解,配制成2 mg/mL的胶原溶液,于4 ℃下10000 r/min离心30 min,取上清液作为供试品溶液,以0.5 mol/L乙酸溶液为空白对照,用紫外分光光度计在200~400 nm范围内进行紫外扫描。
1.2.4.6 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白傅里叶变换红外光谱分析
分别称取鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白适量,与光谱纯KBr混合放在玛瑙研钵中研磨成细粉。取适量混合样品至压片机中压片,将样品置于样品室。用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪对样品在400~4000 cm−1区间内扫描,分辨率设置为2 cm−1。
1.2.4.7 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白圆二色谱分析
分别称取鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白适量,精密称定,加0.5 mol/L乙酸溶解,配制成2 mg/mL的胶原溶液,于4 ℃下10000 r/min离心30 min,取上清液作为供试品溶液,以0.5 mol/L乙酸溶液为空白对照,采用圆二色谱仪于10 ℃进行光谱扫描,比色光程为1 mm,带宽0.5 nm,扫描波长范围为190~260 nm。
1.2.5 鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶对环磷酰胺所致贫血小鼠的改善作用
1.2.5.1 造模及给药方案
依据小鼠体重随机进行分组,分为正常对照组(n=10)和环磷酰胺处理组(n=30)。对环磷酰胺处理组连续4 d腹腔注射80 mg/kg环磷酰胺,造贫血模型,正常组腹腔注射等量的生理盐水。造模完成后,环磷酰胺处理组依据小鼠体重随机分为3组,分别为模型组,鱼鳔胶和驴皮胶给药组[根据人用生药剂量10 g/(60 kg·d),换算成小鼠给药剂量为鱼鳔胶1.52 g/(kg·d)、驴皮胶1.39 g/(kg·d)]。鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶给药组灌胃给药,每天1次,共给药28 d。正常对照组和模型组给予相同体积的纯水。
1.2.5.2 指标检测
实验期间每周称量一次小鼠体重。给药结束后进行眼球后静脉丛取血,全自动模块式血液体液分析仪分析外周血红细胞(RBC)、血红蛋白(HGB)、血小板(PLT)、网织红细胞(RET)等血液学指标。颈椎脱臼处死小鼠(动物伦理审批号:YTU22WT-P06)解剖取出脾脏和胸腺,剥离周围脂肪组织、结缔组织,并用滤纸吸去其表面附着的血液,使用精密电子天平称取脾脏和胸腺的质量,按照下列公式计算脾脏和胸腺系数:脏器系数(%)=脏器质量/体重×100。
1.3 数据处理
实验结果用均值±标准差表示,采用SPSS 21.0统计软件进行t检验及方差分析。P<0.05代表差异具有统计学意义,P<0.01代表差异极显著,采用GraphPad Prism 8.0进行图形绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 鱼鳔、驴皮总蛋白分析结果
蛋白质是人体重要的组成部分,是生命的重要物质基础。胶类物质含有丰富的蛋白质,因此具有较高的营养价值,根据测定结果显示鱼鳔、驴皮总蛋白含量分别为98.00%±0.19%和97.60%±0.21%。
2.2 鱼鳔、驴皮氨基酸组成分析结果
鱼鳔、驴皮均含有17种氨基酸,其总量分别为79.97 g/100 g和77.07 g/100 g(见表1)。鱼鳔和驴皮氨基酸组成相似,含有的苏氨酸、缬氨酸、蛋氨酸、异亮氨酸、亮氨酸、苯丙氨酸、赖氨酸7种必需氨基酸含量占总氨基酸含量的比例分别为17.53%和17.44%,与文献报道中鱼鳔[8]和驴皮[16]的总氨基酸含量和必需氨基酸占比基本一致。而且,二者均以甘氨酸含量最高,谷氨酸、丙氨酸、精氨酸、脯氨酸含量也相对较高。据报道,甘氨酸是血红素合成底物之一,有很好的造血功能[17−18];谷氨酸能够提高机体免疫功能[19−20];丙氨酸通过参与白细胞的代谢影响免疫功能[20];精氨酸具有免疫调节作用,也能够促进生育、生长发育及创伤愈合[21];脯氨酸对保护免疫系统细胞有一定的作用[20]。在鱼鳔和驴皮中,甘氨酸含量分别为20.60、19.70 g/100 g,谷氨酸含量分别为8.85、8.86 g/100 g,丙氨酸含量分别为10.10、7.66 g/100 g,精氨酸含量分别为7.44、6.73 g/100 g,脯氨酸含量分别为9.91、11.10 g/100 g,5种氨基酸总含量达54.00 g/100 g以上。除以上氨基酸外,其他少量氨基酸如天冬氨酸、丝氨酸等能通过不同的途径发挥着调节机体免疫力的作用[20],由此推测鱼鳔和驴皮可能具有补血和增强免疫的功能。
表 1 鱼鳔、驴皮的氨基酸组成(g/100 g)Table 1. Amino acid composition of swim bladder and donkey skin (g/100 g)分类 天冬氨酸 苏氨酸* 丝氨酸 谷氨酸 甘氨酸 鱼鳔 5.15±0.05 2.55±0.05 2.51±0.03 8.85±0.10 20.60±0.17 驴皮 5.01±0.03 1.71±0.05 3.11±0.04 8.86±0.04 19.70±0.11 分类 丙氨酸 胱氨酸 缬氨酸* 蛋氨酸* 异亮氨酸* 鱼鳔 10.10±0.15 0.16±0.01 2.08±0.03 1.22±0.03 0.63±0.02 驴皮 7.66±0.04 0.21±0.01 2.28±0.05 0.29±0.01 1.15±0.03 分类 亮氨酸* 酪氨酸 苯丙氨酸* 赖氨酸* 组氨酸 鱼鳔 2.40±0.07 0.64±0.02 1.75±0.05 3.39±0.06 0.59±0.01 驴皮 2.79±0.05 0.60±0.02 1.86±0.03 3.32±0.09 0.65±0.01 分类 精氨酸 脯氨酸 氨基酸总量 必需氨基酸/总氨基酸 鱼鳔 7.44±0.10 9.91±0.11 79.97±0.52 0.18 驴皮 6.73±0.12 11.10±0.02 77.07±0.07 0.17 注:*为必需氨基酸,表3同。 2.3 鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶分子量分布考察结果
分子量分布考察结果如图1和表2,显示鱼鳔胶分子量范围在50 Da~205 kDa之间,峰位分子量约为12 kDa;驴皮胶分子量范围在50 Da~328 kDa之间,峰位分子量约为14 kDa;鱼鳔胶峰位分子量及分子量范围均小于驴皮胶,推测鱼鳔胶可能比驴皮胶容易被机体吸收。
表 2 鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶分子量分布结果Table 2. Molecular weight distribution results of swim bladder glue and donkey skin glue分类 分子量分布(Da) 峰位分子量(Da) 鱼鳔胶 58~204577 12551 驴皮胶 59~327581 14358 2.4 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白含量、组成及结构分析结果
2.4.1 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白含量
结果显示鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白提取物得率分别为96.14%、28.80%,采用试剂盒法测定提取物中胶原蛋白含量分别为55.01%±0.12%、28.59%±0.09%,经计算鱼鳔、驴皮中胶原蛋白含量分别为52.88%±0.12%、8.12%±0.09%,胃蛋白酶辅助提取法更高效率地提取了鱼鳔胶原蛋白,鱼鳔中胶原蛋白含量约为驴皮中胶原蛋白的6.51倍。
2.4.2 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白氨基酸组成分析
鱼鳔与驴皮胶原蛋白的氨基酸组成如表3所示,组成差异较小,均以甘氨酸的含量最高,占总氨基酸含量的26%以上,分别为14.70、16.20 g/100 g。甘氨酸对于维持胶原蛋白的超螺旋结构具有重要作用,可存在于超螺旋结构的中心且不会发生链变形,使得α-螺旋紧密堆积在一起,形成具有疏水性的超螺旋结构[22−23]。此外,天冬氨酸、谷氨酸、丙氨酸、精氨酸、脯氨酸含量也相对较高,而胱氨酸、蛋氨酸、酪氨酸含量相对较低,以上氨基酸组成结果符合Ⅰ型胶原蛋白特征。
表 3 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白的氨基酸组成(g/100 g)Table 3. Amino acid composition of swim bladder collagen and donkey skin collagen (g/100 g)分类 天冬氨酸 苏氨酸* 丝氨酸 谷氨酸 甘氨酸 鱼鳔胶原蛋白 3.35±0.05 1.73±003 1.67±0.04 6.05±0.05 14.70±0.07 驴皮胶原蛋白 4.06±0.06 1.37±0.03 2.48±0.03 7.24±0.06 16.20±0.03 分类 丙氨酸 胱氨酸 缬氨酸* 蛋氨酸* 异亮氨酸* 鱼鳔胶原蛋白 7.58±0.10 0.05±0.01 1.39±0.04 0.36±0.01 0.35±0.01 驴皮胶原蛋白 6.68±0.02 0.02±0.00 1.80±0.05 0.00 0.93±0.02 分类 亮氨酸* 酪氨酸 苯丙氨酸* 赖氨酸* 组氨酸 鱼鳔胶原蛋白 1.53±0.03 0.13±0.01 1.16±0.02 2.29±0.05 0.51±0.01 驴皮胶原蛋白 2.12±0.04 0.21±0.01 1.36±0.03 2.63±0.03 0.59±0.01 分类 精氨酸 脯氨酸 氨基酸总量 必需氨基酸/总氨基酸 鱼鳔胶原蛋白 5.11±0.03 6.96±0.06 54.92±0.14 0.16 驴皮胶原蛋白 5.16±0.04 8.97±0.07 61.82±0.02 0.16 2.4.3 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白SDS-PAGE电泳
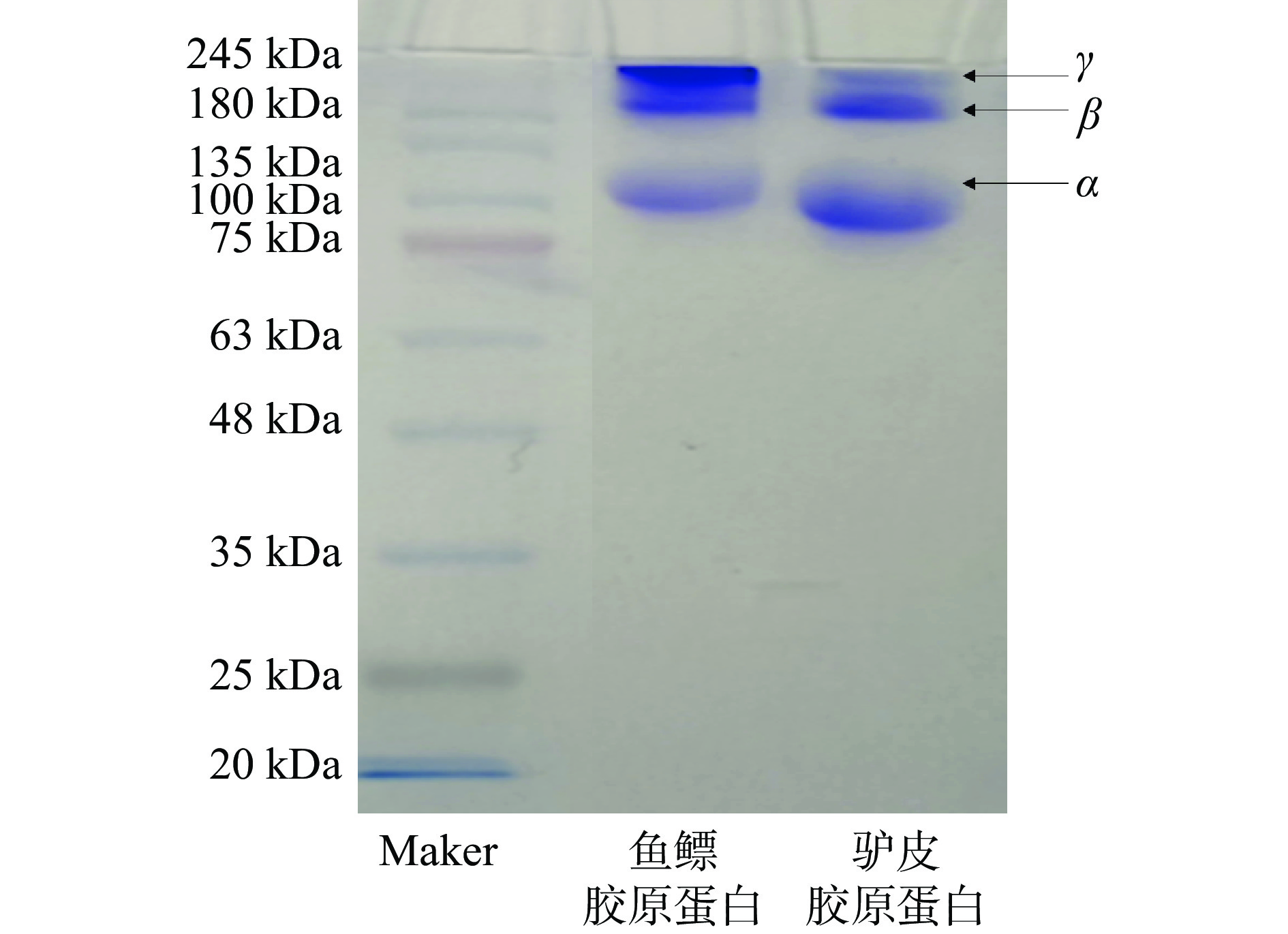
鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白SDS-PAGE电泳结果如图2,鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白中主要含有1条135 kDa左右的α-链,以及由α-链的分子内和分子间交联形成的二聚体β链和三聚体γ链,谱图特征与报道的Ⅰ胶原蛋白[24−26]特征基本一致,可推断提取胶原蛋白为Ⅰ型胶原蛋白。
2.4.4 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白紫外全波长扫描结果分析
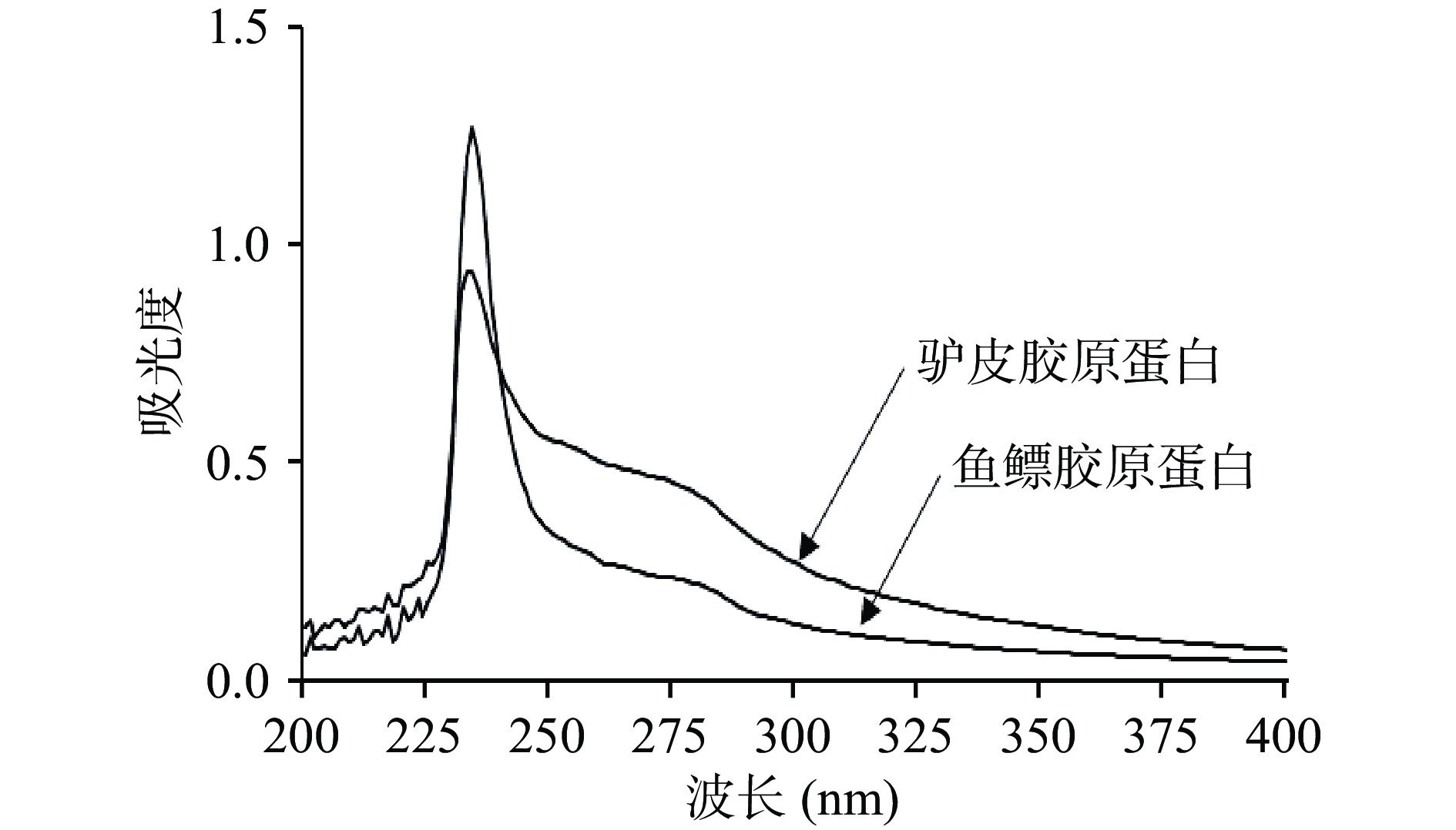
蛋白质的紫外吸收光谱是蛋白质中紫外生色基团加和导致,大多数蛋白质在280 nm处有最大吸收峰[24],这是由于芳香族氨基酸色氨酸残基吲哚环和酪氨酸残基的酚基引起的[26],而Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的特征吸收峰一般在230 nm附近,这主要与胶原多肽链中含有-C=O、-COOH、CO-NH2等生色团有关,由C=O的n→π跃迁所产生。根据紫外吸收图谱(图3)可知鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白紫外最大吸收波长分别在233、232 nm,与杨子帆等[26]测定的鱼鳔胶原蛋白和杨霞等[27]提取的驴皮胶原蛋白的紫外最大吸收波长基本一致,符合Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的特征吸收特点,在280 nm附近存在微弱的吸收,推测可能因少量的芳香族氨基酸引起的,以上结果说明鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白为Ⅰ型胶原蛋白。
2.4.5 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白傅里叶变换红外光谱结果分析
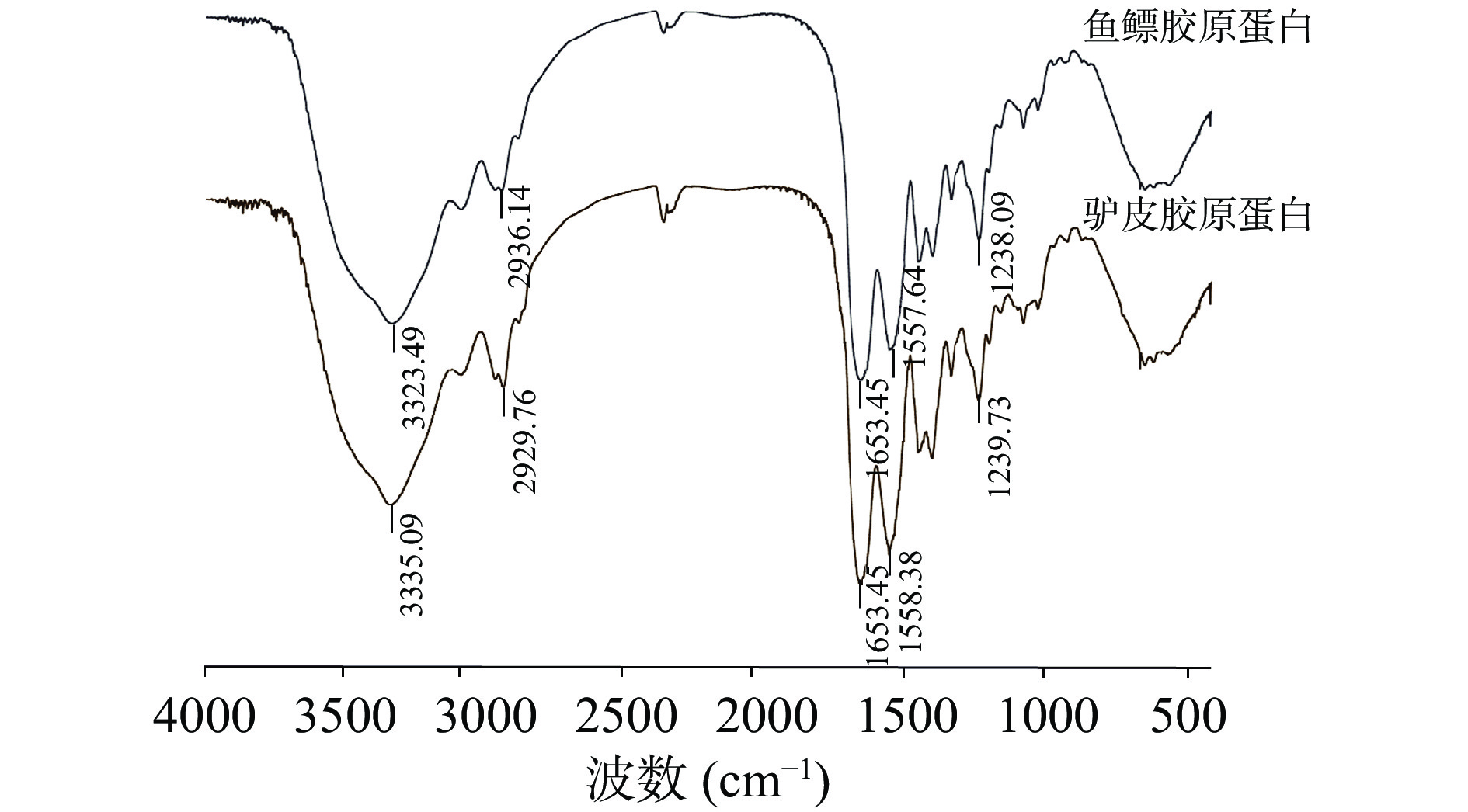
根据傅里叶变换红外光谱分析结果(图4),发现鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白在酰胺A、B以及Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅲ带均可观察到明显的特征峰:分别在3323.49、3335.09 cm−1有吸收,是由分子中N-H伸缩振动与氢键缔合引起,是酰胺A带吸收峰,证明了分子中氢键的存在;分别在2936.14、2929.76 cm−1处有吸收峰,是由于-CH2-的不对称伸缩振动引起的,是酰胺B带吸收峰;酰胺Ⅰ带、Ⅱ带和Ⅲ带可以直接反映蛋白多肽链的构象,根据文献报道,1600~1700 cm−1之间是由于C=O伸缩振动引起的酰胺带的特征吸收峰,是蛋白质二级结构变化的特征区域[28],而鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白均在1653.45 cm−1有特征吸收峰,是酰胺Ⅰ带的吸收峰,表明胶原蛋白的二级结构较好;鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白分别在1557.64、1558.38 cm−1处有吸收峰,是由于C-N伸缩振动或N-H弯曲振动所反应的吸收带,是酰胺Ⅱ带的吸收峰;分别在1238.09、1239.73 cm−1处有吸收峰,是酰胺Ⅲ带的吸收峰,也是胶原蛋白的红外光谱特征吸收峰,这是由于胶原蛋白中甘氨酸和亚氨基酸形成的(Gly-Pro-Hyp)结构引起的[29−30]。
2.4.6 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白圆二色谱结果分析
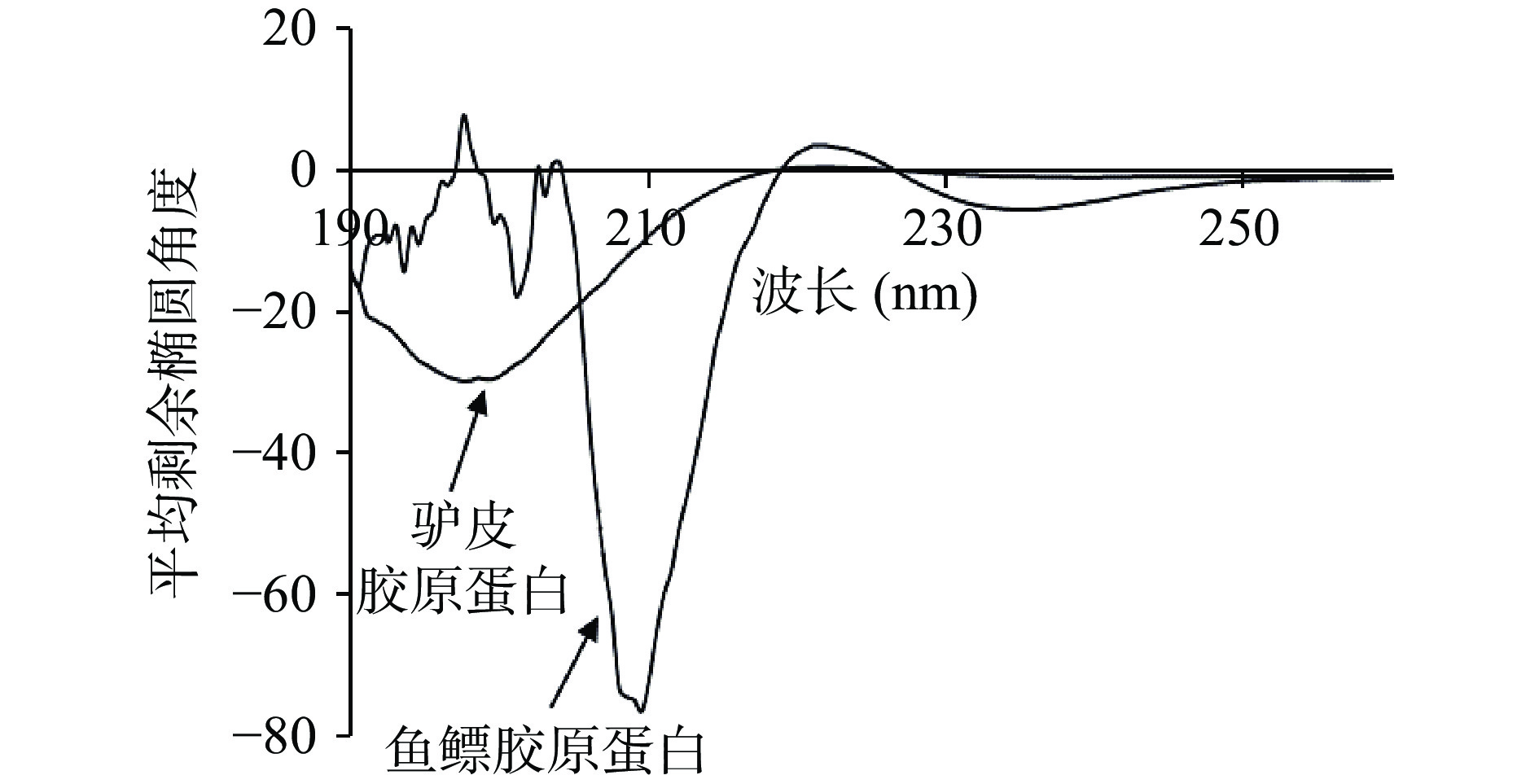
圆二色谱分析结果如图5所示,鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白分别在208、198 nm附近有明显的负吸收峰,在221 nm附近有正吸收峰,具有典型胶原蛋白三螺旋结构的圆二色谱特征峰型;鱼鳔胶原蛋白负峰位置在208 nm附近,而驴皮及其他来源的胶原蛋白负峰一般在198 nm附近[31−32],可能是由于鱼鳔胶原蛋白的三螺旋结构较其他胶原蛋白更紧密[33]。由表4可知,鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白三螺旋结构差别较大,鱼鳔胶原蛋白以α-螺旋为主,驴皮胶原蛋白以β-折叠中的反平行为主。
表 4 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白二级结构分布(%)Table 4. Secondary structure distribution results of swim bladder collagen and donkey skin collagen (%)分类 α-螺旋 反平行 平行 β-转角 无规则 鱼鳔胶原蛋白 94.80 0 0 5.20 0 驴皮胶原蛋白 8.90 57.90 5.80 21.10 6.30 2.5 鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶对环磷酰胺所致贫血小鼠的改善作用研究结果
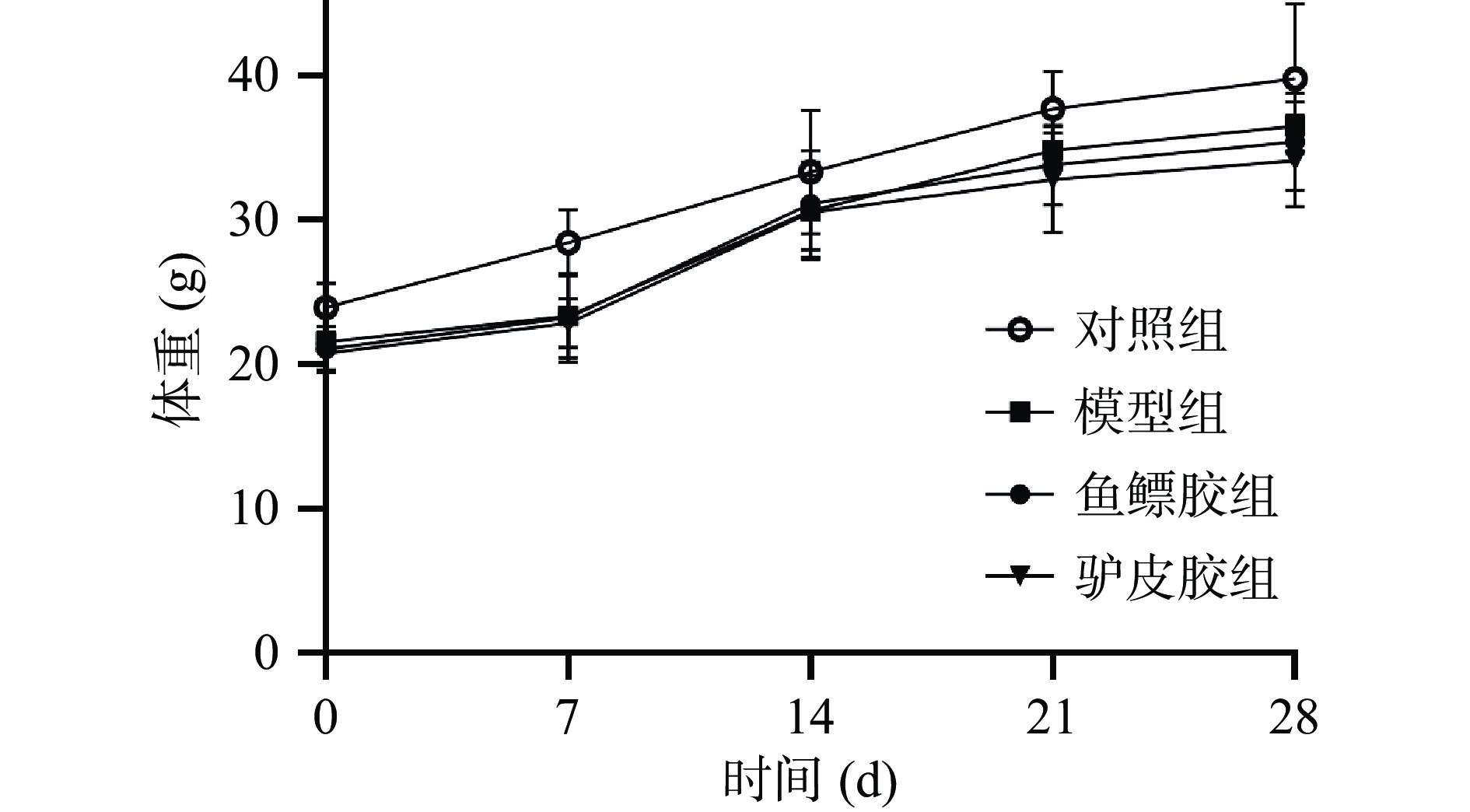
2.5.1 对小鼠体重的影响
实验观察期间各组小鼠精神状态良好,进食饮水排便正常。与正常对照组比较,各组小鼠腹腔注射环磷酰胺后,体重明显降低(P<0.01),随后逐渐恢复并稳步增加,各给药组小鼠体重变化无统计学差异(图6)。
2.5.2 对小鼠器官系数及血液学指标的影响
表5结果显示,与正常对照组相比,模型组小鼠脾脏系数显著升高(P<0.01),胸腺系数显著降低(P<0.01),提示小鼠在注射环磷酰胺后产生免疫抑制,胸腺萎缩,免疫功能下降,同时脾脏代偿性造血呈现肥大,脾脏体积增大;模型组小鼠RBC、HGB、PLT显著降低(P<0.01,P<0.05),代表骨髓抑制后,造血功能被破坏,血液携氧能力下降;RET显著升高(P<0.01),可能因骨髓抑制刺激而提前进入外周血,造成增加异常[34],综合脏器系数和血液学指标的变化说明小鼠贫血造模成功[3]。与模型组相比,鱼鳔胶给药组脾脏系数显著降低、胸腺系数显著升高(P<0.05),且胸腺系数接近正常组水平,RBC、HGB、PLT、RET显著改善(P<0.05),且HGB、PLT指标接近正常对照组水平,无统计学差异;与模型组相比,驴皮胶给药组胸腺系数显著升高(P<0.05),趋近于正常对照组水平,RBC、HGB显著升高(P<0.05),但略低于正常对照组水平。相比驴皮胶组,鱼鳔胶给药组小鼠血液学指标改善显著,且胸腺增大和脾脏萎缩症状均有所缓解,整体评价鱼鳔胶对贫血的改善作用优于驴皮胶。
表 5 鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶对小鼠脾脏系数、胸腺系数、血液学指标的影响Table 5. Effects of swim bladder glue and donkey skin glue on the indexes of spleen, thymus and hematology in mice组别 脾脏系数(%) 胸腺系数(%) RBC(1012/L) HGB(g/L) PLT(109/L) RET(%) 对照组 0.30±0.05 0.27±0.05 10.90±0.85 13.47±2.26 1400.40±367.53 3.29±0.87 模型组 0.56±0.14** 0.17±0.06** 7.60±1.25** 10.52±2.07** 1077.90±208.49* 7.57±2.23** 鱼鳔胶组 0.42±0.09# 0.28±0.06# 9.40±0.93#** 13.14±2.06# 1475.57±363.73# 5.31±2.21#* 驴皮胶组 0.59±0.13** 0.25±0.02# 9.35±1.47#** 11.36±2.09# 1077.88±297.43* 7.35±3.36** 注:与正常对照组比较,*代表P<0.05,**代表P<0.01;与模型组比较,#代表P<0.05。 3. 结论
本文对鱼鳔、驴皮进行了系统的化学成分研究,发现二者总蛋白含量丰富均达97%以上,氨基酸组成差异较小,均以与补血、免疫相关的甘氨酸及谷氨酸等为主;鱼鳔胶分子量相对较小,推测鱼鳔胶更易被机体吸收;鱼鳔中胶原蛋白含量丰富,约为驴皮中胶原蛋白的6.51倍,二者均为Ⅰ型胶原蛋白,但三螺旋结构差异较大,鱼鳔胶原蛋白以α-螺旋为主,驴皮胶原蛋白以反平行为主。
本实验采用腹腔注射环磷酰胺建立小鼠贫血模型,给药28 d后,与模型组相比,鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶组小鼠胸腺系数均显著升高(P<0.05),说明二者能够明显逆转环磷酰胺造成的胸腺萎缩情况,提高机体免疫及造血功能;鱼鳔胶组小鼠脾脏系数显著降低(P<0.05),说明鱼鳔胶对骨髓造血的功能起到了一定程度的改善,脾脏的代偿性造血减少,脾脏体积逐步恢复,而驴皮胶组小鼠脾脏系数改善不显著;鱼鳔胶给药组血液学指标RBC、HGB、PLT、RET均得到显著改善(P<0.05),驴皮胶给药组RBC、HGB显著改善(P<0.05)。以上研究结果证明鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶均可促进环磷酰胺所致贫血小鼠造血机能的恢复,且鱼鳔胶效果优于驴皮胶;结合化学成分比较,二者的分子量大小、氨基酸、胶原蛋白含量及胶原蛋白结构存在较大的不同,推测可能是二者补血活性差异的主要原因,其补血、免疫功效是多成分协同作用的结果,具体的药效物质基础及作用机制还有待深入研究。
-
表 1 鱼鳔、驴皮的氨基酸组成(g/100 g)
Table 1 Amino acid composition of swim bladder and donkey skin (g/100 g)
分类 天冬氨酸 苏氨酸* 丝氨酸 谷氨酸 甘氨酸 鱼鳔 5.15±0.05 2.55±0.05 2.51±0.03 8.85±0.10 20.60±0.17 驴皮 5.01±0.03 1.71±0.05 3.11±0.04 8.86±0.04 19.70±0.11 分类 丙氨酸 胱氨酸 缬氨酸* 蛋氨酸* 异亮氨酸* 鱼鳔 10.10±0.15 0.16±0.01 2.08±0.03 1.22±0.03 0.63±0.02 驴皮 7.66±0.04 0.21±0.01 2.28±0.05 0.29±0.01 1.15±0.03 分类 亮氨酸* 酪氨酸 苯丙氨酸* 赖氨酸* 组氨酸 鱼鳔 2.40±0.07 0.64±0.02 1.75±0.05 3.39±0.06 0.59±0.01 驴皮 2.79±0.05 0.60±0.02 1.86±0.03 3.32±0.09 0.65±0.01 分类 精氨酸 脯氨酸 氨基酸总量 必需氨基酸/总氨基酸 鱼鳔 7.44±0.10 9.91±0.11 79.97±0.52 0.18 驴皮 6.73±0.12 11.10±0.02 77.07±0.07 0.17 注:*为必需氨基酸,表3同。 表 2 鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶分子量分布结果
Table 2 Molecular weight distribution results of swim bladder glue and donkey skin glue
分类 分子量分布(Da) 峰位分子量(Da) 鱼鳔胶 58~204577 12551 驴皮胶 59~327581 14358 表 3 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白的氨基酸组成(g/100 g)
Table 3 Amino acid composition of swim bladder collagen and donkey skin collagen (g/100 g)
分类 天冬氨酸 苏氨酸* 丝氨酸 谷氨酸 甘氨酸 鱼鳔胶原蛋白 3.35±0.05 1.73±003 1.67±0.04 6.05±0.05 14.70±0.07 驴皮胶原蛋白 4.06±0.06 1.37±0.03 2.48±0.03 7.24±0.06 16.20±0.03 分类 丙氨酸 胱氨酸 缬氨酸* 蛋氨酸* 异亮氨酸* 鱼鳔胶原蛋白 7.58±0.10 0.05±0.01 1.39±0.04 0.36±0.01 0.35±0.01 驴皮胶原蛋白 6.68±0.02 0.02±0.00 1.80±0.05 0.00 0.93±0.02 分类 亮氨酸* 酪氨酸 苯丙氨酸* 赖氨酸* 组氨酸 鱼鳔胶原蛋白 1.53±0.03 0.13±0.01 1.16±0.02 2.29±0.05 0.51±0.01 驴皮胶原蛋白 2.12±0.04 0.21±0.01 1.36±0.03 2.63±0.03 0.59±0.01 分类 精氨酸 脯氨酸 氨基酸总量 必需氨基酸/总氨基酸 鱼鳔胶原蛋白 5.11±0.03 6.96±0.06 54.92±0.14 0.16 驴皮胶原蛋白 5.16±0.04 8.97±0.07 61.82±0.02 0.16 表 4 鱼鳔、驴皮胶原蛋白二级结构分布(%)
Table 4 Secondary structure distribution results of swim bladder collagen and donkey skin collagen (%)
分类 α-螺旋 反平行 平行 β-转角 无规则 鱼鳔胶原蛋白 94.80 0 0 5.20 0 驴皮胶原蛋白 8.90 57.90 5.80 21.10 6.30 表 5 鱼鳔胶、驴皮胶对小鼠脾脏系数、胸腺系数、血液学指标的影响
Table 5 Effects of swim bladder glue and donkey skin glue on the indexes of spleen, thymus and hematology in mice
组别 脾脏系数(%) 胸腺系数(%) RBC(1012/L) HGB(g/L) PLT(109/L) RET(%) 对照组 0.30±0.05 0.27±0.05 10.90±0.85 13.47±2.26 1400.40±367.53 3.29±0.87 模型组 0.56±0.14** 0.17±0.06** 7.60±1.25** 10.52±2.07** 1077.90±208.49* 7.57±2.23** 鱼鳔胶组 0.42±0.09# 0.28±0.06# 9.40±0.93#** 13.14±2.06# 1475.57±363.73# 5.31±2.21#* 驴皮胶组 0.59±0.13** 0.25±0.02# 9.35±1.47#** 11.36±2.09# 1077.88±297.43* 7.35±3.36** 注:与正常对照组比较,*代表P<0.05,**代表P<0.01;与模型组比较,#代表P<0.05。 -
[1] 胡海林, 肖丹, 王磊, 等. 龟甲胶对环磷酰胺引起的贫血大鼠的改善作用研究[J]. 中医药信息,2021,8(10):49−52. [HU Hailin, XIAO Dan, WANG Lei, et al. Improvement effect of tortoise shell glue on CTX-induced anemia in rats[J]. Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine,2021,8(10):49−52. HU Hailin, XIAO Dan, WANG Lei, et al . Improvement effect of tortoise shell glue on CTX-induced anemia in rats[J]. Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine,2021 ,8 (10 ):49 −52 .[2] 刘先利, 刘宝利. 基于中医古籍文献探讨血虚证病因、症候及治则治法[J]. 北京中医药, 2020, 39(3):262−265. [LIU Xianli, LIU Baoli. Discussion on causes, symptoms and treatment of blood deficiency syndrome based on ancient Chinese literature[J]. Beijing Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 28(4):28−32. LIU Xianli, LIU Baoli. Discussion on causes, symptoms and treatment of blood deficiency syndrome based on ancient Chinese literature[J]. Beijing Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 28(4): 28−32.
[3] 陈琦, 杨红霞, 李雁, 等. 牦牛皮胶对环磷酰胺致贫血小鼠血象红系参数及脾脏结构的影响[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2019,31(3):415−421. [CHEN Qi, YANG Hongxia, LI Yan, et al. Effects of yak skin gelatin on erythroid parameters and spleen structure of cyclophosphamide-induced anemia mice[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2019,31(3):415−421. CHEN Qi, YANG Hongxia, LI Yan, et al . Effects of yak skin gelatin on erythroid parameters and spleen structure of cyclophosphamide-induced anemia mice[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2019 ,31 (3 ):415 −421 .[4] 忻家础. 动物胶药分类及临床应用[J]. 时珍国药研究,1996(3):56−57. [XIN Jiachu. Classification and clinical application of animal glue[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,1996(3):56−57. XIN Jiachu . Classification and clinical application of animal glue[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,1996 (3 ):56 −57 .[5] 管华诗, 王曙光. 中华海洋本草[M]. 第四卷. 上海:上海科学技术出版社, 2009:246−252. [GUAN Huashi, WANG Shuguang. Chinese marine herb[M]. Volume Ⅳ. Shanghai:Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 2009:246−252. GUAN Huashi, WANG Shuguang. Chinese marine herb[M]. Volume Ⅳ. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 2009: 246−252.
[6] 葛恩会, 刘涛. 鱼鳔功效溯源及其现代研究进展[J]. 中成药,2020,42(9):2403−2406. [GE Enhui, LIU Tao. The efficacy traceability of swim bladder and its modern research progress[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2020,42(9):2403−2406. GE Enhui, LIU Tao . The efficacy traceability of swim bladder and its modern research progress[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2020 ,42 (9 ):2403 −2406 .[7] 邓秋婷, 吴孟华, 张英, 等. 鱼鳔的本草考证[J]. 中药材,2018,41(3):749−752. [DENG Qiuting, WU Menghua, ZHANG Ying, et al. Herbal research of swim bladder[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2018,41(3):749−752. DENG Qiuting, WU Menghua, ZHANG Ying, et al . Herbal research of swim bladder[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2018 ,41 (3 ):749 −752 .[8] 张志军, 王李平, 方军, 等. 花胶营养成分分析及其品质评价[J]. 食品工业,2018,39(7):299−302. [ZHANG Zhijun, WANG Liping, FANG Jun, et al. Analysis and quality evaluation of nutritional components in the fish maw[J]. The Food Industry,2018,39(7):299−302. ZHANG Zhijun, WANG Liping, FANG Jun, et al . Analysis and quality evaluation of nutritional components in the fish maw[J]. The Food Industry,2018 ,39 (7 ):299 −302 .[9] 朱凯悦, 孙娜, 董秀萍, 等. 鱼胶的研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(3):284−290. [ZHU Kaiyue, SUN Na, DONG Xiuping, et al. Research progress of isinglass[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(3):284−290. ZHU Kaiyue, SUN Na, DONG Xiuping, et al . Research progress of isinglass[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022 ,48 (3 ):284 −290 .[10] 段振华, 汪菊兰, 殷安齐, 等. 几种鱼鳔的营养成分分析与评价[J]. 食品研究与开发,2007(10):62−65. [DUAN Zhenhua, WANG Julan, YIN Anqi, et al. Analysis and evaluation of several swim-bladders nutrition components[J]. Food Research and Development,2007(10):62−65. DUAN Zhenhua, WANG Julan, YIN Anqi, et al . Analysis and evaluation of several swim-bladders nutrition components[J]. Food Research and Development,2007 (10 ):62 −65 .[11] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.5-2016食品安全国家标准 食品中蛋白质的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, National Medical Products Administration. GB 5009.5-2016 National standard for food safety Determination of protein in food[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2016. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, National Medical Products Administration. GB 5009.5-2016 National standard for food safety Determination of protein in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[12] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.124-2016食品安全国家标准食品中氨基酸的测定[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2016. [National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, National Medical Products Administration. GB 5009.124-2016 National standard for food safety Determination of amino acids in food[S]. Beijing:China Standards Press, 2016. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, National Medical Products Administration. GB 5009.124-2016 National standard for food safety Determination of amino acids in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[13] 赵峡. 聚古罗糖醛酸硫酸酯及其寡糖的制备、结构与活性研究[D]. 青岛:中国海洋大学, 2007. [ZHAO Xia. A study of the protection of basil polysaccharideto myelosuppression caused by cyclophosphamide chemotherapy[D]. Qingdao:Ocean University of China, 2007. ZHAO Xia. A study of the protection of basil polysaccharideto myelosuppression caused by cyclophosphamide chemotherapy[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2007.
[14] 车帅, 杜芬, 刘楚怡, 等. 中华鲟软骨Ⅱ型胶原蛋白的结构分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(4):60−63. [CHE Shuai, DU Fen, LIU Chuyi, et al. The structure analysis of type Ⅱ collagen from sturgeon ( Acipenser sinensis) cartilage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(4):60−63. CHE Shuai, DU Fen, LIU Chuyi, et al . The structure analysis of type Ⅱ collagen from sturgeon (Acipenser sinensis) cartilage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018 ,39 (4 ):60 −63 .[15] LAEMMLI U K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4[J]. Nature,1970,227(5259):680−685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0
[16] 张磊, 王燕华, 刘畅, 等. 驴皮胶及鹿皮胶的化学品质分析与评价[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(22):57−63. [ZHANG Lei, WANG Yanhua, LIU Chang, et al. Chemical quality analysis and evaluation of donkey hide gelatin and deer skin gelatin[J]. Food Science,2018,39(22):57−63. ZHANG Lei, WANG Yanhua, LIU Chang, et al . Chemical quality analysis and evaluation of donkey hide gelatin and deer skin gelatin[J]. Food Science,2018 ,39 (22 ):57 −63 .[17] ALVES A, BASSOT A, BULTEAU A L, et al. Glycine metabolism and its alterations in obesity and metabolic diseases[J]. Nutrients,2019,11(6):1356. doi: 10.3390/nu11061356
[18] RADIN N S, RITTENBERG D, SHEMIN D. The role of glycine in the biosynthesis of heme[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry,1950,184(2):745−753. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)51009-2
[19] SADELHOFF J J, WIERTSEMA S P, GARSSEN J, et al. Free amino acids in human milk:A potential role for glutamine and glutamate in the protection against neonatal allergies and infections[J]. Frontiers in Immunology,2020,11:1007. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01007
[20] LI, P, YIN Y L, LI D F, et al. Amino acids and immune function[J]. British Journal of Nutrition,2007,98(2):237−252. doi: 10.1017/S000711450769936X
[21] 段秀俊, 刘培, 杨超, 等. 鱼鳔质量标准的提升[J]. 中成药,2020,42(5):1144−1149. [DUAN Xiujun, LIU Pei, YANG Chao, et al. Improvement of quality standard of swim bladder[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2020,42(5):1144−1149. DUAN Xiujun, LIU Pei, YANG Chao, et al . Improvement of quality standard of swim bladder[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2020 ,42 (5 ):1144 −1149 .[22] 冯玲玲, 冯进, 李春阳. 海蜇Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的提取及结构特性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(7):15−21. [FENG Lingling, FENG Jin, LI Chunyang. Extraction and structural characteristics of type I collagen from Rhopilema esculenta[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(7):15−21. FENG Lingling, FENG Jin, LI Chunyang . Extraction and structural characteristics of type I collagen from Rhopilema esculenta[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021 ,42 (7 ):15 −21 .[23] VEERURAJ A, ARUMUGAM M, BALASUBRAMANIAN T. Isolation and characterization of thermostable collagen from the marine eel-fish ( Evenchelys macrura)[J]. Process Biochemistry,2013,48(10):1592−1602. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2013.07.011
[24] 王杉杉, 罗学刚, 苏峰丙, 等. 牦牛皮胶原蛋白的提取及性能分析[J]. 精细化工,2018,35(5):830−837. [WANG Shanshan, LUO Xuegang, SU Fengbing, et al. Extraction and characterization of collagen from the skin of yak[J]. Fine Chemicals,2018,35(5):830−837. WANG Shanshan, LUO Xuegang, SU Fengbing, et al . Extraction and characterization of collagen from the skin of yak[J]. Fine Chemicals,2018 ,35 (5 ):830 −837 .[25] 刘苏锐, 王坤余, 琚海燕. 猪皮Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的提取及其结构表征[J]. 中国皮革,2007(7):43−46, 49. [LIU Surui, WANG Kunyu, JU Haiyan, et al. Isolation and characterization of type Ⅰ collagen from pig skins[J]. China Leather,2007(7):43−46, 49. LIU Surui, WANG Kunyu, JU Haiyan, et al . Isolation and characterization of type Ⅰ collagen from pig skins[J]. China Leather,2007 (7 ):43 −46, 49 .[26] 杨子帆, 张科, 刘莹, 等. 鲟鱼和草鱼鱼鳔酶溶性胶原蛋白的理化性质比较[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(15):27−32. [YANG Zifan, ZHANG Ke, LIU Ying, et al. Comparison of physicochemical properties of pepsin-soluble collagens from swim bladders of sturgeon ( Acipenser schrenckii) and grass carp ( Ctenopharyngodon idella)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(15):27−32. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020110108 YANG Zifan, ZHANG Ke, LIU Ying, et al . Comparison of physicochemical properties of pepsin-soluble collagens from swim bladders of sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii) and grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021 ,42 (15 ):27 −32 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020110108[27] 杨霞, 王珊珊, 赵芙钗, 等. 驴皮中胶原蛋白的提取及其特性[J]. 精细化工,2011,28(9):883−886. [YANG Xia, WANG Shanshan, ZHAO Fuchai, et al. A study on the extraction of collagen from donkey skin and its properties[J]. Fine Chemicals,2011,28(9):883−886. YANG Xia, WANG Shanshan, ZHAO Fuchai, et al . A study on the extraction of collagen from donkey skin and its properties[J]. Fine Chemicals,2011 ,28 (9 ):883 −886 .[28] JEONG H S, VENKATESAN J, KIM S K. Isolation and characterization of collagen from marine fish ( Thunnus obesus)[J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering,2013,18(6):1185−1191. doi: 10.1007/s12257-013-0316-2
[29] 刘丽莉, 马美湖, 杨协力. 牛骨Ⅰ型胶原蛋白提取及结构表征[J]. 食品科学,2010,31(2):87−91. [LIU Lili, MA Meihu, YANG Xieli. Extraction and characterization of type Ⅰ collagen from bovine bone[J]. Food Science,2010,31(2):87−91. LIU Lili, MA Meihu, YANG Xieli . Extraction and characterization of type Ⅰ collagen from bovine bone[J]. Food Science,2010 ,31 (2 ):87 −91 .[30] ZHU S C, YUAN Q J, YANG M T, et al. A quantitative comparable study on multi-hierarchy conformation of acid and pepsin-solubilized collagens from the skin of grass carp ( Ctenopha ryngodon idella)[J]. Mater Science Engineering,2019,96:446−457. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.11.043
[31] 程红, 王玲. 圆二色和拉曼光谱法分析Ⅰ型胶原蛋白二级结构及热变性[J]. 实验室研究与探索,2021,40(5):31−35. [CHENG Hong, WANG Ling. Analysis of the secondary structure and thermal denaturation of type I collagen by CD and Raman spectroscopy[J]. Reserch and Exploration in Laboratory,2021,40(5):31−35. doi: 10.19927/j.cnki.syyt.2021.05.008 CHENG Hong, WANG Ling . Analysis of the secondary structure and thermal denaturation of type I collagen by CD and Raman spectroscopy[J]. Reserch and Exploration in Laboratory,2021 ,40 (5 ):31 −35 . doi: 10.19927/j.cnki.syyt.2021.05.008[32] 刘科, 但卫华, 刘新华, 等. 猪腱Ⅰ型胶原的制备及结构表征[J]. 中国皮革,2014,43(23):9−18. [LIU Ke, DAN Weihua, LIU Xinhua, et al. Preparation and characterization of collagen type I from pig tendons[J]. China Leather,2014,43(23):9−18. LIU Ke, DAN Weihua, LIU Xinhua, et al . Preparation and characterization of collagen type I from pig tendons[J]. China Leather,2014 ,43 (23 ):9 −18 .[33] 钟朝辉, 李春美, 顾海峰, 等. 温度对鱼鳞胶原蛋白二级结构的影响[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2007,27(10):31−35. [ZHONG Zhaohui, LI Chunmei, GU Haifeng, et al. Effect of temperature on the secondary structure of fish scale collagen[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2007,27(10):31−35. ZHONG Zhaohui, LI Chunmei, GU Haifeng, et al . Effect of temperature on the secondary structure of fish scale collagen[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2007 ,27 (10 ):31 −35 .[34] 李晓京, 张时民. 网织红细胞的测定和临床应用[J]. 中国医刊,2007,42(3):63−66. [LI Xiaojing, ZHANG Shimin. Determination and clinical application of reticulocyte[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical,2007,42(3):63−66. LI Xiaojing, ZHANG Shimin . Determination and clinical application of reticulocyte[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical,2007 ,42 (3 ):63 −66 .





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
