Research Progress on the Alleviation of Alcoholic Liver Injury Based on Bibliometric Analysis of Medicinal and Food Homologous Substances
-
摘要: 目的:分析药食同源物质缓解酒精性肝损伤相关领域的研究现状及热点内容,为学者对药食同源物质缓解酒精性肝损伤的深入研究提供思路。方法:采用文献计量学方法,以CNKI、WOS及PubMed数据库为文献源,对自建库起至2022年12月药食同源物质缓解酒精性肝损伤研究领域文献的分布情况进行检索和分析。结果:共检索药食同源物质缓解酒精性肝损伤的中英文文献418篇,专利276项。国内该领域研究起步较晚,但发展速度快,且发文量及专利数量均高于国外,发文量呈指数型结构上升,专利量呈线性结构上升;研究热点主要为葛根、枳椇子、枸杞等药食同源物质缓解酒精性肝损伤的作用机制研究。结论:通过分析药食同源物质缓解酒精性肝损伤文献及专利现状,系统总结了酒精性肝损伤的发病机制,主要与乙醇代谢、氧化应激、免疫炎症反应及肠道屏障受损和菌群失调相关;药食同源物质缓解酒精性肝损伤的作用机制主要与抗脂质过氧化、抗氧化应激反应、抗炎作用及清除自由基、调节肠道菌群有关;未来该领域将以网络药理学、组学技术等技术手段进行更深入的机制研究。Abstract: Objective: This paper analyze the research status and hot contents in the field related to alleviating alcoholic liver injury by medicinal and food homologous substances, and provided ideas for researchers to further in-depth study their alleviation effects on alcoholic liver injury. Methods: By using the bibliometric method, the CNKI, WOS and PubMed databases as the literatures source, the distribution of literatures in the field of alleviating alcoholic liver injury from the establishment of the library to 2022 were searched and analyzed. Results: A total of 418 Chinese and English literature and 276 patents on alleviating alcoholic liver injury with drugs and food homologous substances were obtained. Domestic research in this field started late, but its development speed was fast, and the number of domestic publications and patents were higher than that of foreign countries. The trends in the number of publications and patents showed exponential and linear increase, respectively. The research hotspots mainly focused on the effect mechanism of Kudzu, Hovenia dulcis Thunb., Goji berry and other medicinal and food homologous substances in alleviating alcoholic liver injury. Conclusion: By analyzing the research status of the literature and patent, the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver injury was systematically summary, mainly relate to the ethanol metabolism, oxidative stress, immune inflammatory response and impaired intestinal barrier and dysbacteriosis. The influencing mechanism of medicinal and food homologous substances in alleviating alcoholic liver injury was mainly related to anti-lipid peroxidation, oxidative stress response, anti-inflammatory effect, scavenging of free radicals, and regulation of intestinal flora. In the future, this field would be further studied in the mechanism by network pharmacology, histological techniques and other methods.
-
酒精性肝损伤(Alcoholic Liver Injury,ALI)是由于长期或大量饮酒所致。研究显示,男性乙醇摄入量≥40 g/d,女性乙醇摄入量≥20 g/ d,超过5年,或2周内有暴饮史(乙醇量>80 g/d)即可引起酒精性肝损伤[1]。根据世界卫生组织的报道,全球有20亿人饮酒,其中超过750万人存在滥用酒精的现象。长期过量饮酒危害人体健康[2],从全球来看,超过50%的肝硬化相关死亡率可归因于酒精,通常ALI治疗方式包括酒精戒断、营养补充剂及药物辅助治疗等[3],但长期服用药物会产生一定的副作用,且价格昂贵,治疗范围有限[4]。因此ALI引发的一系列健康问题已引起人们的重视。
研究发现,药食同源物质具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗衰老等多种活性功能,且毒副作用小[5−6]。目前,药食同源物质对ALI的研究主要在保肝、治疗、护肝产品开发等方面,且已有多种药食同源制剂或复方制剂、饮料等应用于临床,如葛根饮料[5]、复方轮叶党参[7]、葛根甘草复合制剂[8]等。与西药相比,药食同源物质能通过多靶点、多途径发挥效用,尤其在改善肝脏功能、抗氧化、抗炎保肝和促进乙醇及脂质代谢等方面疗效显著[6],且其安全性较好。因此,从天然物品中提取并探究有效成分来缓解ALI已成为一个亟待研究的课题。为更好地了解国内外有关药食同源物质缓解ALI领域的研究热点和研究动态,本文采用文献计量学方法,以CNKI、WOS、PubMed数据库为基础,利用VOSviewer及Endnote等工具,对自建库起至2022年的中、英文文献进行定量分析。分析发文量随年份的变化,同时通过关键词聚类方法分析药食同源物质缓解ALI的研究热点,从而系统性整理、综述部分药食同源物质缓解ALI的研究现状。
1. 数据来源及研究方法
1.1 数据收集
文献数据来源途径如表1所示。文章基于CNKI、WOS、PubMed数据库,并结合人工逐一检查,以“酒精肝损伤”、“Alcoholic Liver Injury”为主题检索到论文共计2528篇,以“酒精肝损伤”为主题检索到国内外专利申请为599项,其中筛选出对ALI具有缓解作用的药食同源物质及其提取物与相关成分方面的文献,共计中英文文献418篇,中英文专利276项。
表 1 文献数据来源Table 1. Sources of bibliographic data检索策略 数据收集 文献来源 CNKI、WOS、PubMed数据库 检索策略 以“酒精肝损伤”/“Alcoholic Liver Injury”
为主题进行高级检索检索时间 自建库起至2022年12月31日 收集条件 筛选与药食同源物品缓解ALI有关的期刊论文、学位论文 排除条件 重复文献、无法获取全文、信息明显错误 文献类型 研究性论文(articles)、综述(reviews)、专利(patent) 1.2 研究方法
运用文献计量法。文献收集后,用Endnote建立数据库对文献进行信息整理[9];使用VOSviewer进行可视化图谱制作。从发文量随年份变化、研究热点对药食同源物质缓解ALI相关文献进行梳理,分析其研究现状、热点及趋势。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 药食同源物质缓解酒精性肝损伤研究文献量的年代分布
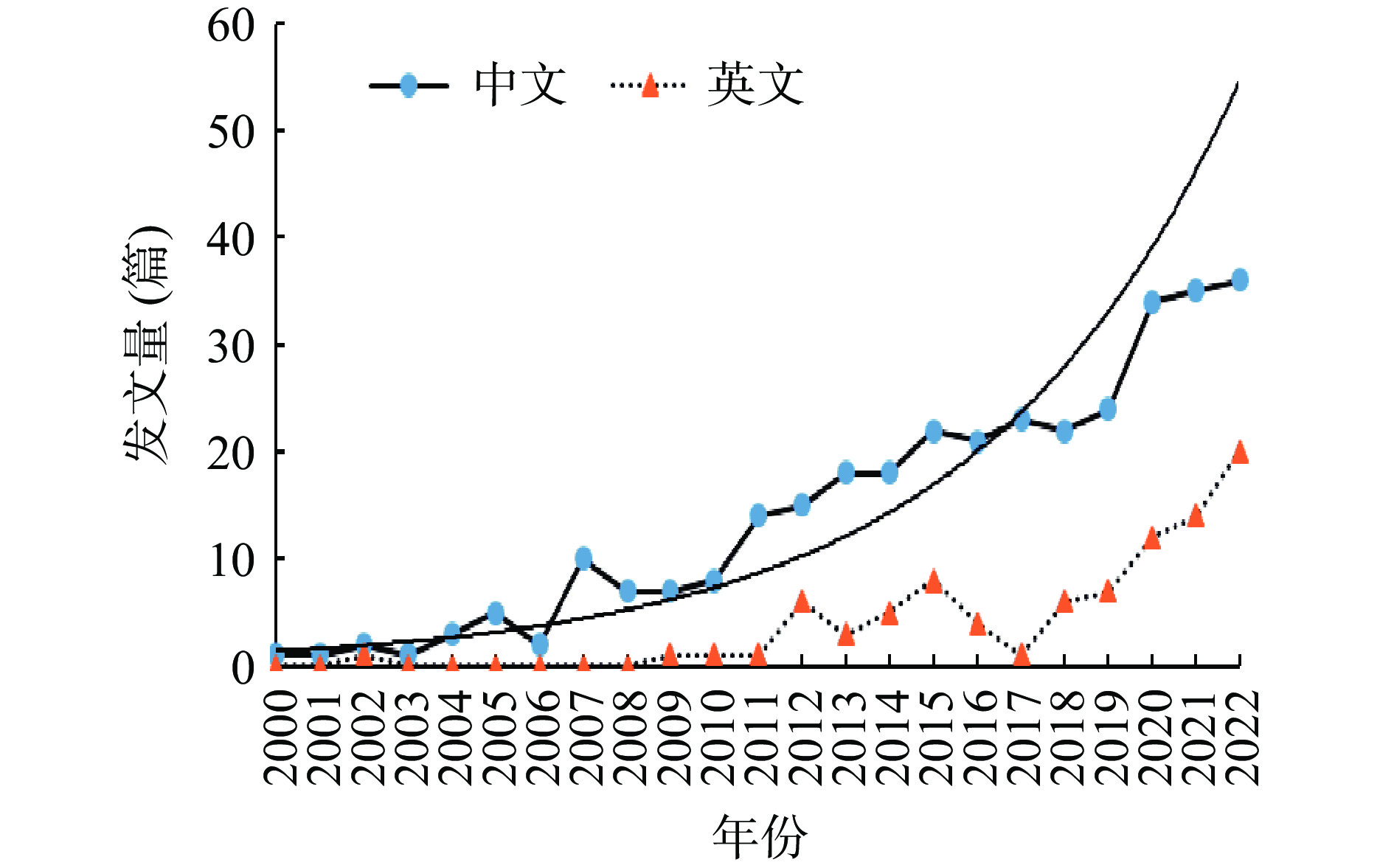
2000~2022年药食同源物质缓解ALI的研究文献量随年份分布趋势如图1所示,中文文献量显著高于英文文献量。就宏观视角而言,中文文献量随年份分布呈指数型上升趋势,而英文文献量随年份分布的态势较为缓慢;就微观视角而言,2000~2006年间的发文量表现出缓慢增加的态势;随着经济、科研技术的发展,人们对药食同源物质及ALI的关注提升,发文量于2007~2022年显著增长,总发文量329篇,年均发文量达21.93篇,较之前有质的提升。
2.2 药食同源物质缓解酒精性肝损伤研究专利量的年代分布
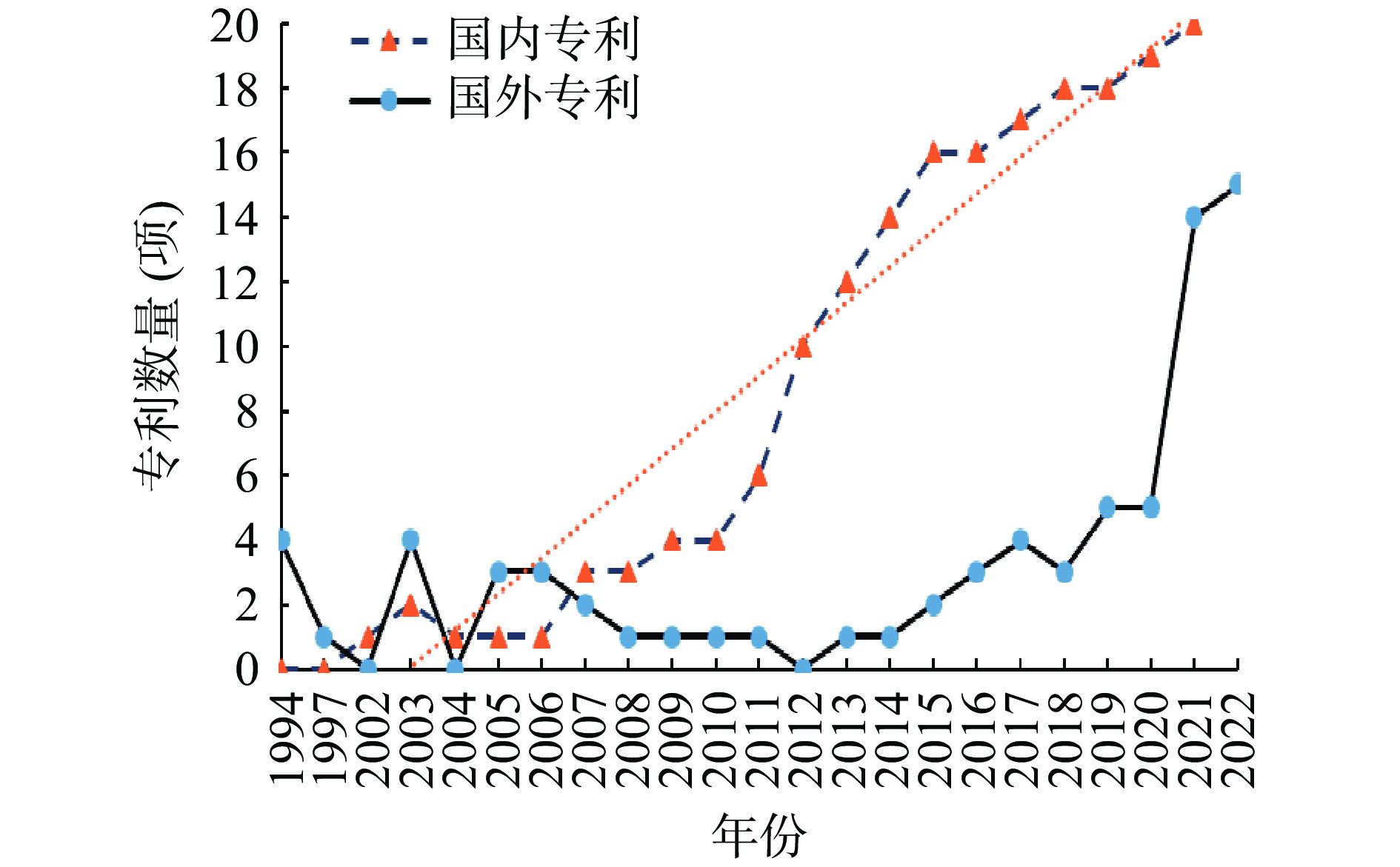
1994~2022年关于药食同源物质缓解ALI专利申请的年代分布如图2所示,国内专利量共213项,国外专利量共63项。总体而言,国内专利量显著高于国外。国内专利量的发展可大致分为两个阶段。第一阶段为2002~2006年,第二阶段为2007年后,该阶段的专利量快速增长,呈线性上升趋势。此外,专利申请量快速增长的同时,其所涉及研究领域和内容随年代也更加多元化,包括药食同源物质缓解ALI的保肝颗粒[10]、护肝片[11]、保肝胶囊[12]、饮料类[13−14](复合饮料/保健饮料)、复方制剂[15]等。
2.3 研究热点分析及其相关综述
2.3.1 药食同源物质缓解酒精性肝损伤的研究热点分析
将检索的中英文期刊,以Endnote的格式导入VOSviewer软件中,对关键词进行共现分析,得到关于“药食同源物质缓解ALI研究”相关文献的可视化分析图。
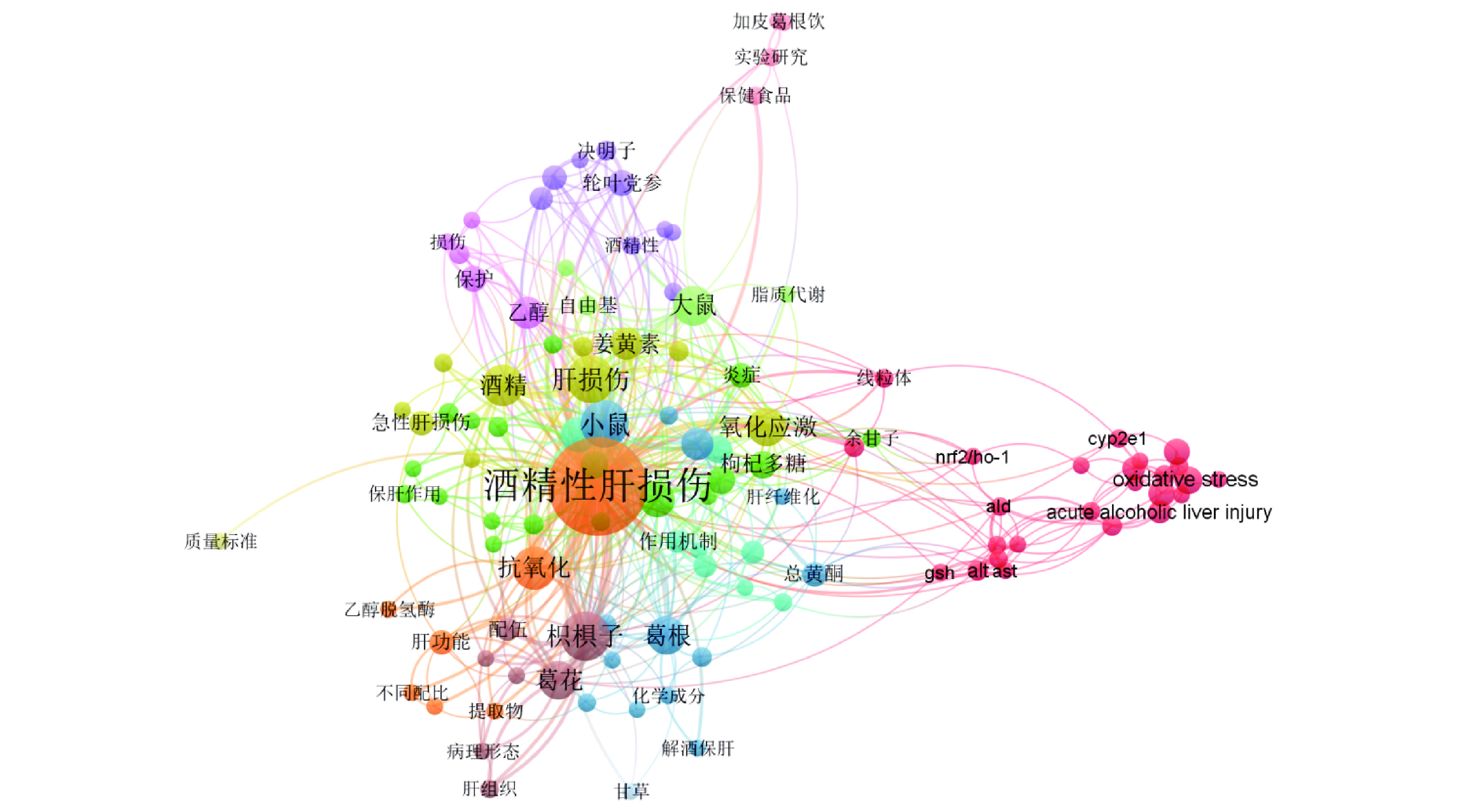
聚类视图表示研究主题之间的联系密切程度、热点关键词,其中关键词字号越大代表聚类程度越强,出现频次越高;圆圈的颜色代表其所属的聚类,不同的聚类用不同的颜色表示。由图3可知,药食同源物质缓解ALI的研究相关文献中出现频次较高的关键词有酒精性肝损伤、葛根、枳椇子、甘草、枸杞、姜黄、山楂、保护作用、作用机制(氧化应激、脂质过氧化、炎症反应)。研究以葛根、枳椇子、枸杞、甘草、姜黄、山楂等药食同源物质缓解ALI为主要内容。
2.3.2 酒精性肝损伤的发病机制分析
目前国内外学者对ALI的发病机制尚未有较为明确的认识,同时也缺乏靶向治疗的方法手段及药物,因此充分了解ALI的发病机制,深入探索药食同源物质缓解ALI的作用机制,有助于科学预防及治疗ALI。根据相关研究发现ALI的发病机制主要与乙醇代谢、氧化应激、炎症反应、肠道菌群与肠道屏障功能相关[3,6],各发病机制之间存在相关性。
2.3.2.1 乙醇代谢
乙醇代谢与ALI的发病机制共有两方面的关联:一方面,酒精代谢主要依靠乙醇脱氢酶(Alcohol Dehydrogenase,ADH)和乙醇氧化酶系统进行氧化代谢[16]。当酒精含量较低时,主要通过ADH进行代谢,而当酒精含量相对较高时,主要通过乙醇氧化酶系统进行代谢,经这两途径代谢会产生高活性物质乙醛,其会在线粒体乙醛脱氢酶作用下生成乙酸并进入三羧酸循环,最终被氧化生成水和二氧化碳;另一方面,酒精在肝脏内代谢时,可将氧化型辅酶Ι转化为还原型辅酶Ι,二者比值被改变,会破化细胞正常的氧化还原状态[6],加快脂肪酸的形成,阻止其氧化,并导致脂肪变性[17]。当大量或长期摄入酒精时,可能会减少乙醛的反应,并降低乙醛脱氢酶活力,从而使其不能正常进行氧化反应代谢,造成乙醛在肝脏内积累,影响乙醇代谢。进一步研究发现,乙醛与ALI的形成有密切关系[18]:a. 乙醛含量过多会影响线粒体功能,进而影响三羧酸循环[6,16];b. 乙醛会影响肝脏的维管系统,抑制微粒蛋白的分泌,导致蛋白和脂质在肝脏中积累[6,16];c. 乙醛能够刺激胶原蛋白的形成,造成肝纤维化[6,16];d. 乙醛进入血液后,在黄嘌呤氧化酶作用下转为超氧化物,自由基水平增加会导致脂质过氧化,进而破坏细胞膜的流动性和通透性,影响酶和受体的功能,造成细胞内膜性结构的破坏[16];e. 乙醛可通过阻碍受损脱氧核糖核酸修复及其胞嘧啶的甲基化,限制细胞分化及受损组织的再生和修复[16,19−20]。
2.3.2.2 氧化应激
氧化应激与ALI的关联主要体现在机体氧化与抗氧化体系的动态失衡。现代药理学研究表明,氧化应激可能是引发ALI的主要因素[21]。氧化应激是指机体受到某些有害条件影响时,比如人体多次或一次过量饮酒,就会导致体内氧化剂和抗氧化剂的动态平衡被打破,导致氧化水平升高从而对肝脏造成损伤[6]。摄入大量酒精,机体内抗氧化剂活性受到抑制,体内自由基(Robot Operating System,ROS)过量积累[22],并与不饱和脂肪酸相互作用,产生脂质过氧化物和蛋白质加合物,导致肝细胞坏死,最终造成严重的酒精相关肝损伤[21]。除了ROS积累导致的氧化应激之外,酒精摄入导致的谷胱甘肽(Glutathione,GSH)减少也会加剧线粒体损伤,干预细胞正常功能[23];此外,铁离子可催化低活性氧化物转化为高活性氧化物,过量酒精会提高铁离子含量,加速肝细胞对铁离子的吸收,进而增强氧化应激作用[24]。酒精本身是一种羟自由基清除剂,其反应产物会影响线粒体通透性并改变膜电势,若长期摄入酒精,其会与抗氧化剂反应,使其失去抗氧化能力,进而加剧酒精性肝损伤[25]。
2.3.2.3 免疫炎症反应
免疫炎症反应与ALI的产生主要与炎症因子(如Tumor nccrosis factor-α (TNF-α)、Human Interleukin-1β (IL-1β)、Interleukin (IL-6))的大量释放有关。当机体发生过度或失控性炎症反应时,能加速ALI恶化;饮酒会引起肠道菌群失调并改变肠道屏障功能,机体内乙醇含量过高会促进肠道部分微生物过度生长,从而使肠粘膜通透性增加,肠道内衍生的内毒素脂多糖(Lipopolysaccharide,LPS)等会通过上皮组织进入血液循环,进而引发一系列炎症反应[7,26]。LPS、ROS等均可与CD14和Toll样受体4(Toll Like Receptor 4,TLR4)发生相互作用,触发信号级联反应,从而刺激Kupffer细胞,分泌促炎细胞因子(如Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB)、TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6等)[6,27],TNF-α是炎症反应中的重要媒介,可激活NF-κB和JNK通路,使肝脏内NF-κB基因促进各种细胞因子的基因转录,进而释放大量的细胞因子和炎症介质,肝脏内的多种细胞因子和炎症介质则会加速肝细胞的炎症浸润、纤维化、肝细胞坏死或凋亡[6,16]。因此,炎症反应在ALI的诱发过程中主要表现为Toll样受体和NOD样受体的活化和炎症因子的大量释放[4]。
2.3.2.4 肠道屏障受损和菌群失调
与肠道相关的ALI发病机制主要包括肠道菌群失调、肠道源性LPS增加、肠道屏障完整性破坏及功能紊乱。酒精的过量摄入影响肠道微生物的数量与组成,造成“菌群失调”,如导致小肠细菌过度生长[28],进而引发机体疾病;酒精还会影响肠屏障,酒精及其代谢物通过影响肠道屏障上的黏液层和紧密连接蛋白的表达[29],对肠屏障完整性产生直接的损害作用。某些微生物代谢物发生改变后也会影响肠道屏障多种防御功能,进而破坏肠道屏障的完整性[30],增加肠道通透性,导致肠道屏障功能受损,造成LPS、活性致病菌和肠内具有促炎作用的代谢物进入体循环,而当这些致病抗原通过门静脉到达肝脏时,便可激活炎症反应等相关病症[31],引发肝损伤恶化,最终形成肝脏相关疾病;另外酒精还可减少短链脂肪酸、小肠上皮粘蛋白和紧密连接蛋白的表达,破坏肠道屏障[31]。此外,饮酒者体内的胆汁酸浓度较高,也会改变肠道通透性[32]。
通过总结ALI主要发病机制,发现各机制之间存在相互影响。目前已有ALI发病机制的综述报道[6,16],但尚不够系统,还需要深入研究其作用机制和预防及治疗方法。
2.3.3 药食同源物质缓解酒精性肝损伤的作用机制分析
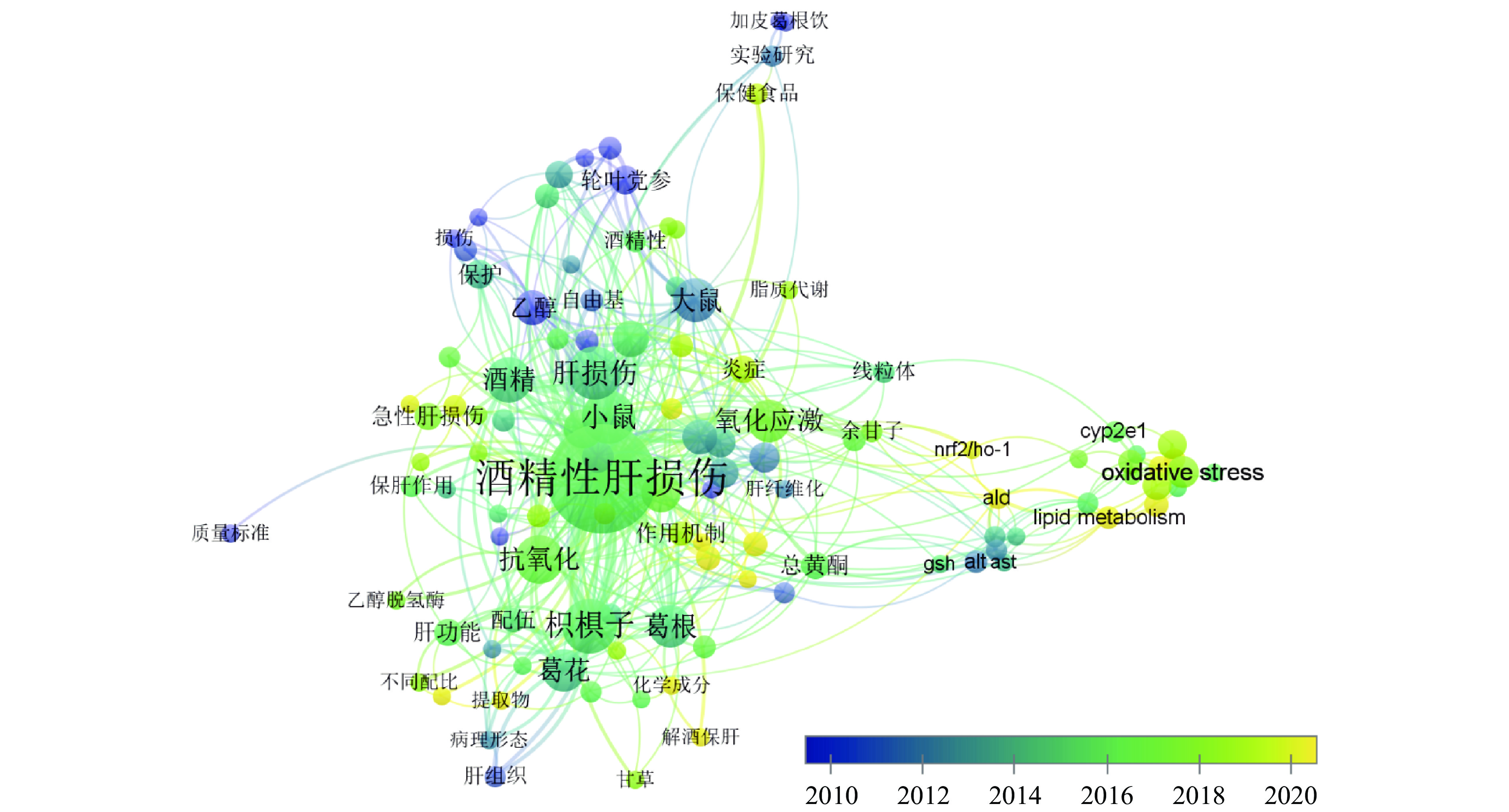
通过图4可视化标签视图分析发现,缓解ALI的药食同源物质主要为葛根、枳椇子、枸杞、甘草、姜黄、山楂、栀子、轮叶党参、肉苁蓉、菊花等,研究方法从简单数据分析到结合组学技术、网络药理学和分子对接等高新技术进行分析研究,作用机制主要与其抗脂质过氧化、抗氧化应激反应、抗炎作用、清除自由基及调节肠道菌群等有关。
2.3.3.1 葛根
葛根可通过主要功效成分异黄酮类化合物及其与其它生物活性物质互作发挥缓解ALI作用[33−35],同时还具有解酒、抗炎、抗氧化及保护心脑血管等功效[26,36]。
以葛根总黄酮对ALI大鼠进行干预,其肝组织脂肪变性明显减轻,谷氨酰转肽酶活性降低,血清谷草转氨酶(Aspartate Transaminase,AST)、谷丙转氨酶(Alanine Transaminase,ALT)活性下降,展现缓解ALI的作用,保护机制研究归因于葛根总黄酮对LPS刺激KC细胞活化产生炎症因子的途径有抑制作用[37]。此外,葛根总黄酮可通过降低大鼠血清高、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇缓解大鼠ALI[38]。
葛根黄酮类化合物的单体成分葛根素对ALI大鼠、小鼠的肝功能、生化、氧化应激、炎症因子指标等均有调控作用,其研究较多。卢雯雯等[39]发现葛根素(1.5 g·kg−1·d−1)能够降低ALI大鼠血清转氨酶和肝纤维化指标,从而发挥其对酒精性肝细胞损伤的保护作用。葛根素还可显著降低大鼠血清中AST、ALT含量,预防大鼠急性ALI,进而保护肝脏[40]。
综上,葛根中的葛根素及葛根黄酮可通过抑制自由基释放、抗脂质过氧化、抗氧化应激反应及抗炎症反应等机制缓解ALI。研究发现葛根多肽同样具有缓解小鼠ALI的作用[41],但目前相关研究较少。
2.3.3.2 枳椇子
枳椇子发挥缓解酒精性肝损伤的主要活性成分为黄酮类化合物[42],其通过与其他物质配伍可更好发挥对ALI的缓解作用[13,41,43−44],枳椇子还具有解酒保肝、醒酒、治疗各种肝病、抗炎抗氧化及抗脂质过氧化等功效[45−47]。张洪等[48]发现枳椇子提取物可通过增强GSH结合反应和超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide Dismutase,SOD)活性显著缓解小鼠急性肝损伤。枳椇子提取物可通过调节肠-肝轴异常,显著抑制TLR4通路及其下游炎症介质,上调肠组织zo-1和occludin的表达发挥保肝作用,可显著逆转乙醇诱导的肠道菌群变化,减少肠源性内毒素的产生,进而缓解大鼠慢性ALI[49]。张永昕等[50]发现枳椇子总黄酮能显著降低大鼠血清中AST、ALT、TNF-α、透明质酸、层粘连蛋白LN含量,减少肝组织产生丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)、提高白细胞介素10(Interleukin,IL-10)水平,减轻酒精引起的炎症反应,进而对酒精引致的肝损伤有良好的防治作用;枳椇子柄多糖表现出相似功效[51],可显著降低ALI小鼠血清AST、ALT与肝脏MDA水平,同时恢复肝脏SOD和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶活性,对急性ALI的缓解作用机制可能与其抗氧化活性有关。
综上,枳椇子可通过抗脂质过氧化、抗氧化应激反应、抗炎反应及调节肠道菌群等机制缓解ALI。虽然已有较多研究表明枳椇子具有缓解ALI的作用,但其发挥保护作用的具体药效物质基础尚不明确。后续可通过网络药理学、分子对接和代谢组学技术深入探究其黄酮类、多糖类、皂苷等生物活性成分发挥缓解ALI作用及其机制。
2.3.3.3 枸杞
枸杞具有抗氧化、保肝、抗脂质过氧化等功效[52−54],相关研究集中于枸杞多糖和黑枸杞黄酮缓解ALI,同时以枸杞为原料制作的饮料、酒及酵素等产品也具有缓解作用[53,55−56]。
红枸杞多糖(Lycium barnarum polysaccharide,LBP)属蛋白多糖、功能性杂多糖[57],具有抗氧化、肝脏保护、免疫调节等功能[58−59]。研究发现,LBP是一种具有潜力的抗ALI药物,可通过清除自由基、抗氧化应激反应、抗炎反应等途径干预ALI[60]。魏芬芬等[52]研究得出LBP能显著降低血清氧化指标,同时提升肝脏MDA、TNF-α、IL-1β、GSH、SOD,从而缓解ALI,可能与清除体内多余自由基、增强体内抗氧化能力及减轻炎症反应相关。LBP可通过调控Nrf2/HO-1信号通路、清除ROS和活性氮的水平及抗凋亡缓解ALI[59]。配伍是提升中成药药效的常用手段之一,任洁[57]与Yan等[61]研究表明,枸杞多糖与硫酸锌复配具有协同作用,可通过促进脂质代谢、抑制氧化应激、炎症反应和调节酒精代谢途径,展现出缓解大鼠ALI的能力。黑枸杞黄酮类化合物具有免疫调节、抗氧化等作用,黑枸杞黄酮可通过NF-κB信号通路减少与TNF-α、IL-6有关的炎症因子,进一步提高IL-10抗炎细胞因子表达量缓解小鼠ALI[62]。
综上,枸杞可通过抑制氧化应激反应、抗炎症反应、调节酒精代谢等途径缓解ALI。其中,红枸杞多糖和黑枸杞黄酮研究较广,但黑枸杞黄酮针对抗炎反应缓解ALI的研究较少。
2.3.3.4 甘草
甘草主要活性成分为三萜类和黄酮类[63],具有保肝、抗氧化、抗炎等功效[34],主要通过甘草酸对ALI起缓解作用,也可利用甘草酸苷与其他物质配伍制成复方制剂[64−65]等起保护作用。
甘草酸是甘草的主要成分之一,又称甘草甜素,为三萜衍生物,其在一定条件下能特异性结合到肝脏,具有抗炎、保肝解毒、减轻肝细胞的损伤、增强免疫等功能[66−68]。甘草酸有两种差向异构体,即18α-甘草酸(18α-Gly)和18β-甘草酸(18β-Gly)。孙晓可等[67,69]研究这两种不同配比的甘草酸对ALI大鼠的影响,发现18α-Gly与18β-Gly在4:6和2:8配比下能显著降低血清ALT、AST、γ-谷氨酰转移酶、乳酸脱氢酶活性和总胆红素、总胆汁酸水平,且此比例下缓解ALI的作用效果更佳。研究发现甘草酸缓解大鼠ALI的作用机制与乙醇分解代谢、肝星状细胞活化、氧化还原酶活性、氨基酸合成代谢、脂肪酸的生物合成、Notch信号通路等功能或通路有关,可通过调节多基因可变剪切缓解ALI病变[68]。
甘草苷是甘草中的主要黄酮类化合物,具有保护心脏系统等功效[63]。但甘草苷缓解ALI的作用研究较少,张芬芬等[63]研究其对急性灌胃小鼠肝损伤的防治作用,发现甘草苷可有效提高小鼠血清ADH水平和肝脏ADH、SOD水平,并推测这可能与甘草苷可一定程度上改善脂质过氧化、增强受损肝脏抗氧化能力、减少炎症反应有关,但机制还需要进一步研究。
综上,甘草缓解ALI的研究主要集中于甘草酸与甘草苷,与抗脂质过氧化、抗氧化应激反应及抗炎反应等机制有关。其中以甘草酸苷为原料之一制成甘草酸苷复方制剂及以甘草酸为原料的研究较多,甘草苷缓解ALI的研究较少且作用机制不明确,探究其作用机制对预防和治疗ALI具有重要意义。
2.3.3.5 姜黄
姜黄素是姜黄的主要生物活性成分,可作为抗氧化剂及消炎药在中草药治疗中使用[70]。主要通过抑制内质网应激、抗氧化应激反应、抗炎及抗脂质过氧化等方式缓解ALI。尹蓉[71]发现姜黄素能通过抑制酒精中毒大鼠脂质过氧化和肝组织中NF-κB的表达,从而减轻或防治酒精诱导的肝损伤;郑修齐等[72]发现姜黄素可抑制ALI小鼠肝脏中ROS的表达,减少相关炎症反应的发生,判断其通过抑制内质网应激缓解ALI。曾瑜等[73]发现姜黄素能增强急性酒精中毒小鼠的体内抗氧化能力从而发挥对ALI的保护作用。原海忠等[74]和韩刚等[75−76]制备姜黄素固体分散体,发现其对ALI大鼠具有保护作用。
2.3.3.6 山楂
山楂中对ALI起缓解作用的功效成分主要是山楂黄酮类化合物及山楂酸。山楂黄酮具有抗氧化、调节脂质代谢、护肝等多种药理活性[77]。研究发现,山楂叶总黄酮主要通过清除自由基及抗脂质过氧化等缓解ALI。李素婷等[78−81]研究发现山楂黄酮可降低小鼠血清指标,提高SOD、GSH含量并改善肝组织脂肪变性和炎症坏死,对酒精所导致的急性肝损伤有一定的保护作用,机制与清除自由基,抑制脂质过氧化反应有关。常陆林[82]发现山楂黄酮可降低ALT、AST、MDA、TNF-α水平,增加SOD,缓解ALI,其机制与降低小鼠血清自由基水平、抑制脂质过氧化有关;潘莹等[83]发现山楂总黄酮缓解ALI机制与其对自由基的拮抗作用、脂质代谢有关。
山楂酸是一种抗氧化剂,具有抗氧化、抗炎等广泛的生物活性[84]。研究发现,山楂酸主要通过抗氧化应激反应缓解ALI。魏蕾等[84]研究发现山楂酸可降低急性ALI小鼠体内MDA含量、提高GSH含量,增强机体自身的抗氧化能力来缓解肝损伤;Yan等[85]发现山楂酸可通过抑制CYP2E1、NF-κB通路降低酒精引起的急性肝脏氧化应激反应和炎症应激反应缓解ALI。
综上,山楂缓解ALI的研究主要集中于山楂黄酮与山楂酸,与清除自由基、抗脂质过氧化、抗氧化应激反应等机制有关。
2.3.3.7 其他药食同源物质
根据药食同源物质缓解ALI文献分析,还有灵芝、人参、黄芪、铁皮石斛等具有缓解ALI作用。
灵芝具有保肝护肝、预防乙醇性肝损伤、抗氧化等功能[86]。灵芝的子实体和菌丝体对ALI大鼠、小鼠肝损伤模型具有良好的保护作用,其重要的药理活性成分为灵芝多糖和灵芝三萜类化合物[86]。灵芝多糖具有抗炎、调节免疫、抗氧化、保护肝脏等药理作用[87],主要通过抗炎、抗氧化应激反应及抗脂质过氧化等方式缓解ALI。叶丽云等[88]建立了小鼠急性ALI模型研究发现灵芝多糖能够有效预防急性ALI,作用机制可能与调节GSH代谢、细胞色素P450、视黄醇代谢相关基因的表达有关;赵婷婷等[89]研究发现,灵芝菌丝体多糖可通过改善小鼠肝脏氧化应激水平和脂质代谢水平、降低小鼠肝脏细胞炎症因子含量,发挥其对ALI的缓解作用。灵芝三萜类化合物对ALI保护作用的活性成分主要为灵芝三萜(GLA)及灵芝酸,其通过抗自由基作用、抗氧化应激反应抗炎、抗脂质过氧化及调节肠道菌群等缓解ALI。魏晓霞[90]发现GLA能降低急性ALI小鼠血清中ALT、AST含量及肝指数,降低肝组织MDA含量、提高SOD活性,具有保护肝细胞膜、抗自由基作用,表明其对肝损伤小鼠有明显的保护作用;Lü等[91]和Cao等[92]均发现灵芝酸可通过调节肠道菌群紊乱或肠道微生物组成缓解小鼠ALI。另有研究发现灵芝酸A对小鼠急性ALI的作用机制可能与调控脂代谢、抑制氧化应激、减轻炎症反应、抑制Toll/NF-κB信号通路和凋亡信号通路相关蛋白表达有关[93]。综上,灵芝中的多糖、三萜组分及灵芝酸A主要通过抗氧化、抗炎、抗脂质过氧化、清除自由基及调节肠道菌群等作用缓解ALI,但其发挥效果的具体作用机制尚不清楚,且鲜有利用组学技术研究其作用机制,后续可从该方面深入探索。
人参具有抗氧化、提高免疫力、保肝等作用[94],其主要活性成分为人参皂苷类化合物[95],包括人参皂苷Re、Rh1、Rg1等。张宇等[96]发现高浓度(40 mg/kg)人参皂苷CK可明显改善ALI大鼠肝脏组织病理病变,通过抑制内质网应激反应、酒精刺激大鼠肝脏引起的细胞凋亡及线粒体结构损伤及脂肪病变程度缓解ALI;李明珂等[97]发现人参皂苷Rh1及CK可降低肝酶水平、延缓肝细胞病理改变、减轻肝细胞脂肪变性程度及改善线粒体结构与功能;尹春金[98]和Gao等[99]发现人参皂苷Re、Rg1缓解ALI作用机制可能与其增强Nrf2-ARE通路的氧化防御系统有关。综上,人参皂苷缓解酒精诱导的大小鼠肝损伤,作用机制主要与改善肝组织病变及脂肪堆积、保护线粒体结构与功能、抗氧化应激反应等有关。
3. 结论与展望
通过对CNKI、WOS、PubMed自建库起至2022年主题为“酒精肝损伤”的研究文献进行检索,筛选得到418篇文献、276项专利,分析发现:国内文献量及专利申请量显著高于国外,说明我国在药食同源物质缓解ALI方面的研究具有显著优势,国外文献量增长缓慢,2012年开始稍有增长;药食同源物质缓解ALI领域的研究热点、关键词聚类分析等表明,其研究物质热点集中于葛根、枳椇子、枸杞、甘草、姜黄等,研究内容热点为药食同源物质缓解ALI的保护作用机制。通过综述ALI的发病机制和葛根、枳椇子、枸杞、甘草、姜黄等药食同源物质及其有效成分缓解ALI的作用机制研究,得其发病机制主要与乙醇代谢、氧化应激、炎症反应、肠道相关,药食两用物质作用机制主要与降酶、抗脂质过氧化、抗氧化应激反应、抗炎作用、清除自由基及调节肠道菌群有关,且药食同源物质有效成分中的多糖类、黄酮类及三萜类化合物对该领域的研究较多,多肽类化合物鲜少关注。
总之,该领域的研究还需要更深入的探索,如特定药食同源物质缓解ALI的具体有效成分、靶向作用机制尚不清楚;大部分研究为体内实验证明药食同源物质可缓解ALI,但相关的体外细胞实验、毒理学研究较少;目前仅少量文献从分子水平进行研究验证,未来可从代谢、转录、基因及结合新的分析方法(如组学技术、网络药理学和分子对接)等方面进行深入研究;未来将发掘更多药食同源物质及其有效成分来缓解ALI,并研究出更多安全健康药食同源复方制剂、保健饮料等用于预防及缓解肝损伤。
-
表 1 文献数据来源
Table 1 Sources of bibliographic data
检索策略 数据收集 文献来源 CNKI、WOS、PubMed数据库 检索策略 以“酒精肝损伤”/“Alcoholic Liver Injury”
为主题进行高级检索检索时间 自建库起至2022年12月31日 收集条件 筛选与药食同源物品缓解ALI有关的期刊论文、学位论文 排除条件 重复文献、无法获取全文、信息明显错误 文献类型 研究性论文(articles)、综述(reviews)、专利(patent) -
[1] 王政, 葛冰洁, 王萌, 等. 中药对酒精性肝损伤的保护作用研究进展[J]. 延边大学农学学报,2019,41(3):102−108. [WANG Z, GE B J, WANG M, et al. Research progress on the protective effect of traditional Chinese medicine on alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Agronomy of Yanbian University,2019,41(3):102−108. WANG Z, GE B J, WANG M, et al . Research progress on the protective effect of traditional Chinese medicine on alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Agronomy of Yanbian University,2019 ,41 (3 ):102 −108 .[2] REHM J, MATHERS C, POPOVA S, et al. Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcoholuse disorders[J]. The Lancet,2009,373(9682):2223−2233. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60746-7
[3] 相君妍. 五味子提取物对酒精性肝病小鼠的干预作用及其机制研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2022. [XIANG J Y. Intervention effect and mechanism of Schisandra extract in mice with alcoholic liver disease[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2022. XIANG J Y. Intervention effect and mechanism of Schisandra extract in mice with alcoholic liver disease[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2022.
[4] 吴云霞, 耿敬章, 王志男, 等. 基于文献计量的黄酒研究现状分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(21):327−335. [WU Y X, GENG J Z, WANG Z N, et al. Analysis of research status of rice wine based on bibliometrics[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(21):327−335. WU Y X, GENG J Z, WANG Z N, et al . Analysis of research status of rice wine based on bibliometrics[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022 ,43 (21 ):327 −335 .[5] 徐菁阳, 汪宇. 葛根饮料对小鼠酒精性肝损伤保护作用研究[J]. 海峡药学,2017,29(1):28−31. [XU J Y, WANG Y. Protective effect of Kudzu Drink on alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Straits Pharmacy,2017,29(1):28−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3765.2017.01.010 XU J Y, WANG Y . Protective effect of Kudzu Drink on alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Straits Pharmacy,2017 ,29 (1 ):28 −31 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3765.2017.01.010[6] 韩丽, 饶智, 曹林, 等. 部分药食同源食物防治酒精性肝损伤研究进展[J]. 中国食物与营养,2023,29(2):57−62. [HAN L, RAO Z, CAO L, et al. Research progress on the prevention and treatment of alcoholic liver injury with some medicinal and food homologous foods[J]. Food and Nutrition in China,2023,29(2):57−62. HAN L, RAO Z, CAO L, et al . Research progress on the prevention and treatment of alcoholic liver injury with some medicinal and food homologous foods[J]. Food and Nutrition in China,2023 ,29 (2 ):57 −62 .[7] 张亮. 复方轮叶党参对酒精性肝损伤的预防作用及机制研究[D]. 延吉:延边大学, 2007. [ZHANG L. Preventive effect and mechanism of compound Codonopsis albiflora on alcoholic liver injury[D]. Yanji:Yanbian University, 2007. ZHANG L. Preventive effect and mechanism of compound Codonopsis albiflora on alcoholic liver injury[D]. Yanji: Yanbian University, 2007.
[8] 夏勇, 鹿伟, 傅剑云, 等. 葛根甘草复合制剂预防酒精性肝损伤的作用研究[J]. 浙江预防医学,2010,22(11):13−15. [XIA Y, LU W, FU J Y, et al. Effect of Kudzu licorice compound preparation in preventing alcoholic liver injury[J]. Zhejiang Preventive Medicine,2010,22(11):13−15. XIA Y, LU W, FU J Y, et al . Effect of Kudzu licorice compound preparation in preventing alcoholic liver injury[J]. Zhejiang Preventive Medicine,2010 ,22 (11 ):13 −15 .[9] 郑金萍, 李君, 周瑶. 基于文献计量学的ICU患者肠内喂养不耐受国内研究现状分析[J]. 护理实践与研究,2022,19(22):3353−3358. [ZHENG J P, LI J, ZHOU Y. Analysis of domestic research status of enteral feeding intolerance in ICU patients based on bibliometrics[J]. Nursing Practice and Research,2022,19(22):3353−3358. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9676.2022.22.008 ZHENG J P, LI J, ZHOU Y . Analysis of domestic research status of enteral feeding intolerance in ICU patients based on bibliometrics[J]. Nursing Practice and Research,2022 ,19 (22 ):3353 −3358 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9676.2022.22.008[10] 吕双双, 廉伟伟, 刘金海, 等. 杞枣养肝颗粒对大鼠酒精性肝损伤模型的影响[J]. 化工设计通讯,2023,49(3):206−208. [LÜ S S, LIAN W W, LIU J H, et al. Effect of jujube liver granules on model of alcoholic liver injury in rats[J]. Chemical Design Communications,2023,49(3):206−208. LÜ S S, LIAN W W, LIU J H, et al . Effect of jujube liver granules on model of alcoholic liver injury in rats[J]. Chemical Design Communications,2023 ,49 (3 ):206 −208 .[11] 王晨, 宋立孝, 程金来, 等. 葛菊护肝片通过调节NF- κB和Bcl-2/Bax信号通路改善酒精所致的小鼠肝脏损伤[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2023,29(18):17−25. [WANG C, SONG L X, CHENG J L, et al. Ge Ju liver protection tablets improve alcohol-induced liver injury in mice by regulating NF- κB and Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathways[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Medical Formulae,2023,29(18):17−25. WANG C, SONG L X, CHENG J L, et al . Ge Ju liver protection tablets improve alcohol-induced liver injury in mice by regulating NF-κB and Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathways[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Medical Formulae,2023 ,29 (18 ):17 −25 .[12] 王振基, 孟小倩, 刘文亚, 等. 野菊花保肝胶囊抗乙肝病毒及抗酒精性肝损伤的作用[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版),2017,52(5):549−553. [WANG Z J, MENG X Q, LIU W Y, et al. Effect of wild chrysanthemum capsule against hepatitis B virus and alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Health Sciences),2017,52(5):549−553. WANG Z J, MENG X Q, LIU W Y, et al . Effect of wild chrysanthemum capsule against hepatitis B virus and alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Zhengzhou University (Health Sciences),2017 ,52 (5 ):549 −553 .[13] 王睿, 刘丽达, 蒋勇, 等. 枳椇子五味子复合饮料对酒精肝损伤有辅助保护功能的研究[J]. 公共卫生与预防医学,2017,28(6):34−36. [WANG R, LIU L D, JIANG Y, et al. Study on the auxiliary protective function of schisandra compound drink on alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Public Health and Preventive Medicine,2017,28(6):34−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2483.2017.06.009 WANG R, LIU L D, JIANG Y, et al . Study on the auxiliary protective function of schisandra compound drink on alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Public Health and Preventive Medicine,2017 ,28 (6 ):34 −36 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2483.2017.06.009[14] 祝冬青, 黄亚东. 葛根保健饮料的研制及其对大鼠酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国酿造,2008,201(24):50−53. [ZHU D Q, HUANG Y D. Development of pueraria kudzu health drink and its protective effect on alcoholic liver injury in rats[J]. China Brewing,2008,201(24):50−53. ZHU D Q, HUANG Y D . Development of pueraria kudzu health drink and its protective effect on alcoholic liver injury in rats[J]. China Brewing,2008 ,201 (24 ):50 −53 .[15] 白雪松. 轮叶党参复方制剂预防酒精性肝损伤作用机制研究[D]. 延吉:延边大学, 2005. [BAI X S. Study on the mechanism of action of Codonopsis albiflora compound preparation in preventing alcoholic liver injury[D]. Yanji:Yanbian University, 2005. BAI X S. Study on the mechanism of action of Codonopsis albiflora compound preparation in preventing alcoholic liver injury[D]. Yanji: Yanbian University, 2005.
[16] 曲航, 高鑫, 伊娟娟, 等. 食源性天然产物对酒精性肝损伤的防护作用研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(17):283−290. [QU H, GAO X, YI J J, et al. Research progress on protective effects of foodborne natural products on alcoholic liver injury[J]. Food Science,2020,41(17):283−290. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190920-262 QU H, GAO X, YI J J, et al . Research progress on protective effects of foodborne natural products on alcoholic liver injury[J]. Food Science,2020 ,41 (17 ):283 −290 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190920-262[17] GUENGERICH F P. Cytochrome P450 2E1 and its roles in disease[J]. Chemico-Biological Interactions,2020,322:109056. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109056
[18] TESCHKE R. Alcoholic liver disease:Alcohol metabolism, cascade of molecular mechanisms, cellular targets, and clinical aspects[J]. Biomedicines,2018,6(4):106. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines6040106
[19] 季光, 尤圣富, 王磊, 等. 清肝活血方对肝星状细胞增殖及胶原生成的影响[J]. 中西医结合肝病杂志,2006,16(1):23−25. [JI G, YOU S F, WANG L, et al. Effects of liver cleansing and blood revitalization on proliferation and collagen production of hepatic stellate cells[J]. Journal of Integrative Medicine and Hepatology,2006,16(1):23−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2006.01.009 JI G, YOU S F, WANG L, et al . Effects of liver cleansing and blood revitalization on proliferation and collagen production of hepatic stellate cells[J]. Journal of Integrative Medicine and Hepatology,2006 ,16 (1 ):23 −25 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-0264.2006.01.009[20] 王晓英. Cao(2+)信号转导在急性乙醛性肝损伤发病机制作用中的探讨[D]. 济南:山东大学, 2008. [WANG X Y. Discussion on the pathogenesis of Cao(2+) signal transduction in acute acetaldehyde liver injury[D]. Jinan:Shandong University, 2008. WANG X Y. Discussion on the pathogenesis of Cao(2+) signal transduction in acute acetaldehyde liver injury[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2008.
[21] 孟文文, 刘慧茹, 张文光, 等. 中药防治酒精性肝病作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中草药,2022,53(3):868−881. [MENG W W, LIU H R, ZHANG W G, et al. Research progress on the mechanism of action of traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention and treatment of alcoholic liver disease[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2022,53(3):868−881. MENG W W, LIU H R, ZHANG W G, et al . Research progress on the mechanism of action of traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention and treatment of alcoholic liver disease[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2022 ,53 (3 ):868 −881 .[22] 李园园, 华艳芳, 周俊英. 酒精性肝病发病机制[J]. 临床荟萃,2016,31(7):723−726. [LI Y Y, HUA Y F, ZHOU J Y. Pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease[J]. Clinical Focus,2016,31(7):723−726. LI Y Y, HUA Y F, ZHOU J Y . Pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease[J]. Clinical Focus,2016 ,31 (7 ):723 −726 .[23] BROWN G C. Regulation of mitochondrial respiration by nitric oxide inhibition of cytochrome coxidase[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta,2001,1504(1):46−57. doi: 10.1016/S0005-2728(00)00238-3
[24] WHITFIELD J B, ZHU G, HEATH A C, et al. Effects of alcohol consumption on indices of iron stores and of iron stores on alcohol intake markers[J]. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research, 2001, 25(7):1037-1045.
[25] ZHANG Y, LU Y, JI H, et al. Anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative stress and novel therapeutic targets for cholestatic liver injury[J]. Bioscience Trends, 2019, 13(1):23−31.
[26] 苑程鲲, 沈文娟, 吴效科, 等. 葛根素临床应用新进展[J]. 中医药信息,2011,28(6):125−127. [YUAN C K, SHEN W J, WU X K, et al. New progress in clinical application of puerarin[J]. Information of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2011,28(6):125−127. doi: 10.19656/j.cnki.1002-2406.2011.06.053 YUAN C K, SHEN W J, WU X K, et al . New progress in clinical application of puerarin[J]. Information of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2011 ,28 (6 ):125 −127 . doi: 10.19656/j.cnki.1002-2406.2011.06.053[27] SZABO G, LIPPAI D. Converging actions of alcohol on liver and brain immune signaling[J]. International Review of Neurobiology,2014,118(7):359−380.
[28] BODE C, BODE J C. Effect of alcohol consumption on the gut[J]. Research Clinical Gastroenterology,2003,17(4):575−592.
[29] 吴亚, 李艳茹, 杨寄镯, 等. 酒精性肝病发病机制研究现状[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志,2020,36(12):2822−2825. [WU Y, LI Y R, YANG J B, et al. Research status on the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease[J]. Journal of Clinical Hepatobiliary Diseases,2020,36(12):2822−2825. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.12.038 WU Y, LI Y R, YANG J B, et al . Research status on the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease[J]. Journal of Clinical Hepatobiliary Diseases,2020 ,36 (12 ):2822 −2825 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5256.2020.12.038[30] XIE G, ZHONG W, ZHENG X, et al. Chronic ethanol consumption alters mammalian gastrointestinal content metabolites[J]. Journal of Proteome Research,2013,12(7):3297−3306. doi: 10.1021/pr400362z
[31] BAJAJ J S, KAKIYAMA G, ZHAO D, et al. Continued alcohol misuse in human cirrhosis is associated with an impaired gut-liver axis[J]. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research,2017,41(11):1857−1865. doi: 10.1111/acer.13498
[32] BAJAJ J S. Alcohol, liver disease and the gut microbiota[J]. Nature Reviews Gastroenterol Hepatology,2019,16(4):235−246. doi: 10.1038/s41575-018-0099-1
[33] 陈东亚, 陆罗定, 徐军, 等. 葛根牛磺酸复合片对小鼠酒精性肝损伤的作用[J]. 江苏预防医学,2016,27(2):139−140,235. [CHEN D Y, LU L D, XU J, et al. Effect of pueraria kudzu taurine compound on alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Jiangsu Preventive Medicine,2016,27(2):139−140,235. doi: 10.13668/j.issn.1006-9070.2016.02.004 CHEN D Y, LU L D, XU J, et al . Effect of pueraria kudzu taurine compound on alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Jiangsu Preventive Medicine,2016 ,27 (2 ):139 −140,235 . doi: 10.13668/j.issn.1006-9070.2016.02.004[34] 王煜, 周吉银, 周世文. 含葛根解酒方剂的机制研究进展[J]. 中国药房,2007,180(18):1424−1426. [WANG Y, ZHOU J Y, ZHOU S W. research progress on the mechanism of pueraria Kudzu-containing hangover[J]. China Pharmacy,2007,180(18):1424−1426. WANG Y, ZHOU J Y, ZHOU S W . research progress on the mechanism of pueraria Kudzu-containing hangover[J]. China Pharmacy,2007 ,180 (18 ):1424 −1426 .[35] 王恒禹, 刘玥, 沈孝坤, 等. 葛根的解酒作用及应用[J]. 中国医疗前沿,2012,7(20):7−9. [WANG H Y, LIU Y, SHEN X K, et al. Hangover effect and application of kudzu[J]. China Medical Frontiers,2012,7(20):7−9. WANG H Y, LIU Y, SHEN X K, et al . Hangover effect and application of kudzu[J]. China Medical Frontiers,2012 ,7 (20 ):7 −9 .[36] 王艳丽, 宁宇, 丁莹. 中医药治疗酒精性肝病研究进展[J]. 中医药信息,2022,39(9):80−84. [WANG Y L, NING Y, DING Y. Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of alcoholic liver disease[J]. Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine,2022,39(9):80−84. doi: 10.19656/j.cnki.1002-2406.20220914 WANG Y L, NING Y, DING Y . Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of alcoholic liver disease[J]. Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine,2022 ,39 (9 ):80 −84 . doi: 10.19656/j.cnki.1002-2406.20220914[37] 崔团, 彭景华, 唐亚军, 等. 葛根总黄酮对Lieber-Decarli酒精性肝损伤大鼠库普弗细胞活化信号通路的干预作用[J]. 上海中医药大学学报,2011,25(3):71−75. [CUI T, PENG J H, TANG Y J, et al. Intervention effect of pueraria total flavonoids on kuppfer cell activation signaling pathway in lieber-decarli alcoholic liver injury rats[J]. Journal of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2011,25(3):71−75. doi: 10.16306/j.1008-861x.2011.03.019 CUI T, PENG J H, TANG Y J, et al . Intervention effect of pueraria total flavonoids on kuppfer cell activation signaling pathway in lieber-decarli alcoholic liver injury rats[J]. Journal of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2011 ,25 (3 ):71 −75 . doi: 10.16306/j.1008-861x.2011.03.019[38] 张国哲, 季建伟, 刘平平, 等. 葛根、葛花及其总黄酮对酒精性肝病大鼠防治作用研究[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2020,22(11):29−32. [ZHANG G Z, JI J W, LIU P P, et al. Study on the prevention and treatment effect of kudzu, kudzu and their total flavonoids on rats with alcoholic liver disease[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Chinese Medicine,2020,22(11):29−32. doi: 10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2020.11.007 ZHANG G Z, JI J W, LIU P P, et al . Study on the prevention and treatment effect of kudzu, kudzu and their total flavonoids on rats with alcoholic liver disease[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Chinese Medicine,2020 ,22 (11 ):29 −32 . doi: 10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2020.11.007[39] 卢雯雯, 陈玖, 吴国琳, 等. 葛根素对酒精性肝损伤大鼠血清转氨酶及肝纤维化指标的影响[J]. 浙江中医杂志,2008,442(1):7−9. [LU W W, CHEN J, WU G L, et al. Effect of puerarin on serum transaminases and liver fibrosis indexes in rats with alcoholic liver injury[J]. Zhejiang Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2008,442(1):7−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0411-8421.2008.01.003 LU W W, CHEN J, WU G L, et al . Effect of puerarin on serum transaminases and liver fibrosis indexes in rats with alcoholic liver injury[J]. Zhejiang Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2008 ,442 (1 ):7 −9 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0411-8421.2008.01.003[40] 季红, 郭鑫, 尹鹏. 葛根素对急性酒精性肝损伤的预防作用[J]. 医学综述,2016,22(15):3048−3049,3055,3121. [JI H, GUO X, YIN P. Preventive effect of puerarin on acute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Medical Review,2016,22(15):3048−3049,3055,3121. JI H, GUO X, YIN P . Preventive effect of puerarin on acute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Medical Review,2016 ,22 (15 ):3048 −3049,3055,3121 .[41] 柳海艳. 葛花枳椇子配伍对酒精性肝损伤的防治作用及机理探讨[D]. 北京:北京中医药大学, 2011. [LIU H Y. Effect and mechanism of Agaricus dzu on alcoholic liver injury[D]. Beijing:Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2011. LIU H Y. Effect and mechanism of Agaricus dzu on alcoholic liver injury[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2011.
[42] 吴名草, 郁星, 沈旭丹, 等. 葛根枳椇子植物饮料对小鼠酒精性肝损伤的保护作用研究[J]. 粮油食品科技,2022,30(4):157−163. [WU M C, YU X, SHEN X D, et al. Protective effect of pueraria mirifica hovenia dulcis botanical drink on alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Cereals, Oils and Food Science and Technology,2022,30(4):157−163. doi: 10.16210/j.cnki.1007-7561.2022.04.021 WU M C, YU X, SHEN X D, et al . Protective effect of pueraria mirifica hovenia dulcis botanical drink on alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Cereals, Oils and Food Science and Technology,2022 ,30 (4 ):157 −163 . doi: 10.16210/j.cnki.1007-7561.2022.04.021[43] 李志满, 臧爱梅, 沙纪越, 等. 西洋参枳椇子配伍对急性酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(1):375−380. [LI Z M, ZANG A M, SHA J Y, et al. Protective effect of American ginseng in acute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(1):375−380. LI Z M, ZANG A M, SHA J Y, et al . Protective effect of American ginseng in acute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022 ,43 (1 ):375 −380 .[44] 梁玉琼, 黄庆, 梁小勤. 复方枳椇子制剂对急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠的保护作用[J]. 时珍国医国药,2020,31(1):72−74. [LIANG Y Q, HUANG Q, LIANG X Q. Protective effect of compound Citrus aurantium preparations in mice with acute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Shizhen Chinese Medicine and Medicine,2020,31(1):72−74. LIANG Y Q, HUANG Q, LIANG X Q . Protective effect of compound Citrus aurantium preparations in mice with acute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Shizhen Chinese Medicine and Medicine,2020 ,31 (1 ):72 −74 .[45] 嵇杨, 杨平, 李俊. 枳椇子对乙醇所致小鼠肝脏损伤的预防作用[J]. 中药药理与临床,2000,15(3):19−20. [JI Y, YANG P, LI J. Preventive effect of Citrus aurantium on ethanol-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Pharmacology and Clinical Medicine of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica,2000,15(3):19−20. doi: 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2000.03.011 JI Y, YANG P, LI J . Preventive effect of Citrus aurantium on ethanol-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Pharmacology and Clinical Medicine of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica,2000 ,15 (3 ):19 −20 . doi: 10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2000.03.011[46] 王晓倩. 枳椇子化学成分及其生物活性研究[D]. 宜春:宜春学院, 2022. [WANG X Q. Study on chemical composition and biological activity of Citrus aurantium[D]. Yichun:Yichun University, 2022. WANG X Q. Study on chemical composition and biological activity of Citrus aurantium[D]. Yichun: Yichun University, 2022.
[47] 胡晓慧, 唐志书, 吴群军, 等. 基于网络药理学和分子对接技术的枳椇子防治酒精性肝病分子机制研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2021,32(9):1309−1320. [HU X H, TANG Z S, WU Q J, et al. Molecular mechanism of Citrus aurantium in the prevention and treatment of alcoholic liver disease based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology[J]. New Drugs and Clinical Pharmacology of Traditional Chinese Medicines,2021,32(9):1309−1320. doi: 10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2021.09.011 HU X H, TANG Z S, WU Q J, et al . Molecular mechanism of Citrus aurantium in the prevention and treatment of alcoholic liver disease based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology[J]. New Drugs and Clinical Pharmacology of Traditional Chinese Medicines,2021 ,32 (9 ):1309 −1320 . doi: 10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2021.09.011[48] 张洪, 何文 , 李志建. 枳椇子提取物对乙醇所致小鼠肝损伤的拮抗作用[J]. 广东药学院学报, 2001, 16(3):180−181. [ZHANG H, HE W, LI Z J. Antagonistic effect of Citrus auraria extract on ethanol-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Journal of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2001, 16(3):180−181. ZHANG H, HE W, LI Z J. Antagonistic effect of Citrus auraria extract on ethanol-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Journal of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, 2001, 16(3): 180−181.
[49] QIU P, DONG Y, ZHU T, et al. Semen hoveniae extract ameliorates alcohol-induced chronic liver damage in rats via modulation of the abnormalities of Gut-Liver Axis[J]. Phytomedicine,2019,52(4):40−50.
[50] 张永昕, 俞发. 枳椇子总黄酮治疗酒精性肝病及其作用机制研究[J]. 中药材,2010,33(11):1782−1785. [ZHANG Y X, YU F. Study on the mechanism of total flavonoids in the treatment of alcoholic liver disease[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2010,33(11):1782−1785. ZHANG Y X, YU F . Study on the mechanism of total flavonoids in the treatment of alcoholic liver disease[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2010 ,33 (11 ):1782 −1785 .[51] WANG M C, ZHU P L, JIANG C X, et al. Preliminary characterization, antioxidant activity in vitro and hepatoprotective effect on acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice of polysaccharides from the peduncles of Hovenia dulcis[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2012,50(9):2964−2970. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2012.06.034
[52] 魏芬芬, 王文娟, 贺青华, 等. 枸杞多糖对小鼠酒精性肝损伤的保护作用及机制研究[J]. 药物评价研究,2019,42(5):852−857. [WEI F F, WANG W J, HE Q H, et al. Protective effect and mechanism of goji berry polysaccharide on alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Pharmacological Evaluation Research,2019,42(5):852−857. WEI F F, WANG W J, HE Q H, et al . Protective effect and mechanism of goji berry polysaccharide on alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Pharmacological Evaluation Research,2019 ,42 (5 ):852 −857 .[53] 赵嘉庆, 史春丽, 王立英, 等. 枸杞酒多糖的提取、成分测定及其对酒精性肝病的影响研究[J]. 中国酿造,2020,39(10):114−118. [ZHAO J Q, SHI C L, WANG L Y, et al. Extraction, composition determination of Goji wine polysaccharides and their effects on alcoholic liver disease[J]. China Brewing,2020,39(10):114−118. ZHAO J Q, SHI C L, WANG L Y, et al . Extraction, composition determination of Goji wine polysaccharides and their effects on alcoholic liver disease[J]. China Brewing,2020 ,39 (10 ):114 −118 .[54] 宋育林, 曾民德, 陆伦根, 等. 枸杞多糖防治大鼠酒精性肝病的形态学观察[J]. 医学研究生学报,2002,14(1):13−16,95-96. [SONG Y L, ZENG M D, LU L G, et al. Morphological observation of goji polysaccharides in the prevention and treatment of alcoholic liver disease in rats[J]. Journal of Graduate Medical Sciences,2002,14(1):13−16,95-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8199.2002.01.004 SONG Y L, ZENG M D, LU L G, et al . Morphological observation of goji polysaccharides in the prevention and treatment of alcoholic liver disease in rats[J]. Journal of Graduate Medical Sciences,2002 ,14 (1 ):13 −16,95-96 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8199.2002.01.004[55] 冯琳, 常明, 唐年初. 不同菌种发酵枸杞酵素对酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(17):98−104. [FENG L, CHANG M, TANG N C. Protective effect of fermented goji berry enzymes in different cultures on alcoholic liver injury[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2021,47(17):98−104. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.026803 FENG L, CHANG M, TANG N C . Protective effect of fermented goji berry enzymes in different cultures on alcoholic liver injury[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2021 ,47 (17 ):98 −104 . doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.026803[56] 胡戈, 曹建民, 周海涛, 等. 黑果枸杞汁对大鼠酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国应用生理学杂志,2022,38(3):241−246. [HU G, CAO J M, ZHOU H T, et al. Protective effect of goji berry juice on alcoholic liver injury in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Physiology,2022,38(3):241−246. doi: 10.12047/j.cjap.6242.2022.035 HU G, CAO J M, ZHOU H T, et al . Protective effect of goji berry juice on alcoholic liver injury in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Physiology,2022 ,38 (3 ):241 −246 . doi: 10.12047/j.cjap.6242.2022.035[57] 任洁. 硫酸锌/枸杞多糖对大鼠慢性酒精性肝损伤的协同保护作用[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2014. [REN J. Synergistic protective effect of zinc sulfate/goji polysaccharide on chronic alcoholic liver injury in rats[D]. Yangling:Northwest A&F University, 2014. REN J. Synergistic protective effect of zinc sulfate/goji polysaccharide on chronic alcoholic liver injury in rats[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2014.
[58] 江冠宇. 枸杞水提物对急性酒精肝损伤的保护作用研究[D]. 银川:宁夏大学. [JIANG G Y. Protective effect of goji berry water extract on acute alcoholic liver injury[D]. Yinchuan:Ningxia University. JIANG G Y. Protective effect of goji berry water extract on acute alcoholic liver injury[D]. Yinchuan: Ningxia University.
[59] 张铃浩. 枸杞多糖对酒精性肝损伤的保护作用及机制研究[D]. 兰州:兰州大学, 2019. [ZHANG L H. Protective effect and mechanism of goji polysaccharides on alcoholic liver injury[D]. Lanzhou:Lanzhou University, 2019. ZHANG L H. Protective effect and mechanism of goji polysaccharides on alcoholic liver injury[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019.
[60] CHENG D, KONG H. The effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on alcohol-induced oxidative stress in rats[J]. Molecules,2011,16(3):2542−2550. doi: 10.3390/molecules16032542
[61] YAN Y, WU W, LU L, et. al. Study on the synergistic protective effect of Lycium barbarum L. polysaccharides and zinc sulfate on chronic alcoholic liver injury in rats[J]. Food Science and Nutrition,2019,7(11):3435−3442. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1182
[62] 李娣. 基于NF-κB通路研究有氧运动与黑枸黄酮对酒精性肝损伤小鼠的干预及组织差异表达[D]. 长沙:湖南师范大学, 2018. [LI D. Study on the intervention and tissue differential expression of aerobic exercise and black citrus flavonoids in mice with alcoholic liver injury based on NF-κB pathway[D]. Changsha:Hunan Normal University, 2018. LI D. Study on the intervention and tissue differential expression of aerobic exercise and black citrus flavonoids in mice with alcoholic liver injury based on NF-κB pathway[D]. Changsha: Hunan Normal University, 2018.
[63] 张芬芬, 程梦迪, 周珊珊, 等. 甘草苷对急性灌酒小鼠肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 阜阳师范大学学报(自然科学版),2021,38(2):69−72,84. [ZHANG F F, CHENG M D, ZHOU S S, et al. Protective effect of glycyrrhizin on liver injury in acute perfusion mice[J]. Journal of Fuyang Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2021,38(2):69−72,84. ZHANG F F, CHENG M D, ZHOU S S, et al . Protective effect of glycyrrhizin on liver injury in acute perfusion mice[J]. Journal of Fuyang Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2021 ,38 (2 ):69 −72,84 .[64] 孟巍, 韩璐, 任世成. 复方甘草酸苷对亚急性酒精性肝损伤大鼠的保护作用研究[J]. 公共卫生与预防医学,2011,22(3):8−11. [MENG W, HAN L, REN S C. Protective effect of compound glycyrrhizinate glycyrrhizin in rats with subacute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Public Health and Preventive Medicine,2011,22(3):8−11. MENG W, HAN L, REN S C . Protective effect of compound glycyrrhizinate glycyrrhizin in rats with subacute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Public Health and Preventive Medicine,2011 ,22 (3 ):8 −11 .[65] 孟巍, 王柏军, 任世成. 复方甘草酸苷对大鼠酒精性肝损伤的预防作用研究[J]. 中国医药指南,2013,11(3):482−483. [MENG W, WANG B J, REN S C. Preventive effect of compound glycyrrhizin on alcoholic liver injury in rats[J]. Chinese Medical Guide,2013,11(3):482−483. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8194.2013.03.379 MENG W, WANG B J, REN S C . Preventive effect of compound glycyrrhizin on alcoholic liver injury in rats[J]. Chinese Medical Guide,2013 ,11 (3 ):482 −483 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8194.2013.03.379[66] 张霞, 程富胜. 甘草提取物对酒精性肝损伤的防治作用研究[J]. 中兽医医药杂志,2013,32(6):10−14. [ZHANG X, CHENG F S. Preventive effect of licorice extract on alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine,2013,32(6):10−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6354.2013.06.002 ZHANG X, CHENG F S . Preventive effect of licorice extract on alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine,2013 ,32 (6 ):10 −14 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6354.2013.06.002[67] 孙晓可, 杨飒, 孟祥波, 等. 不同配比18 α-与18 β-甘草酸对酒精性肝损伤大鼠肝功能的影响[J]. 江西师范大学学报(自然科学版),2018,42(2):166−170. [SUN X K, YANG S, MENG X B, et al. Effects of different ratios of 18 α- and 18 β-glycyrrhizic acid on liver function in rats with alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Jiangxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2018,42(2):166−170. SUN X K, YANG S, MENG X B, et al . Effects of different ratios of 18α- and 18β-glycyrrhizic acid on liver function in rats with alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Jiangxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2018 ,42 (2 ):166 −170 .[68] 从美丽, 古丽拉莱·多力坤, 周蓓, 等. 应用基因芯片技术分析甘草酸改善大鼠酒精性肝损伤的作用机制[J]. 医学动物防制,2022,38(4):374−378. [CONG M L, GULLAI DORIKUN, ZHOU B, et al. Analysis of the mechanism of glycyrrhizic acid in improving alcoholic liver injury in rats by gene chip technology[J]. Medical Animal Control,2022,38(4):374−378. CONG M L, GULLAI DORIKUN, ZHOU B, et al . Analysis of the mechanism of glycyrrhizic acid in improving alcoholic liver injury in rats by gene chip technology[J]. Medical Animal Control,2022 ,38 (4 ):374 −378 .[69] 孙晓可, 杨飒, 霍小位, 等. 甘草酸对酒精性肝损伤大鼠脏器的保护作用:18 α-与18 β-甘草酸配比的影响[J]. 现代食品科技,2018,34(7):21−27. [SUN X K, YANG S, HUO X W, et al. Protective effect of glycyrrhizic acid on organs in rats with alcoholic liver injury:Effect of 18 α- and 18 β-glycyrrhizic acid ratio[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2018,34(7):21−27. SUN X K, YANG S, HUO X W, et al . Protective effect of glycyrrhizic acid on organs in rats with alcoholic liver injury: Effect of 18α- and 18β-glycyrrhizic acid ratio[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2018 ,34 (7 ):21 −27 .[70] SIDDIQUI M A, AHAMED M, AHMAD J, et. al. Nickel oxide nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and apoptosis in cultured human cells that is abrogated by the dietary antioxidant curcumin[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2012,50(3-4):641−647. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2012.01.017
[71] 尹蓉. 姜黄素对酒精性肝损伤保护作用的实验研究[D]. 兰州:兰州大学, 2008. [YIN R. Experimental study on the protective effect of curcumin on alcoholic liver injury[D]. Lanzhou:Lanzhou University, 2008. YIN R. Experimental study on the protective effect of curcumin on alcoholic liver injury[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2008.
[72] 郑修齐, 吕小会, 张鑫, 等. 姜黄素通过抑制内质网应激对酒精诱导的小鼠肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 贵州医药,2021,45(5):675−678. [ZHENG X Q, LÜ X H, ZHANG X, et al. Protective effects of curcumin on alcohol-induced liver injury in mice through inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Guizhou Medicine,2021,45(5):675−678. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-744X.2021.05.001 ZHENG X Q, LÜ X H, ZHANG X, et al . Protective effects of curcumin on alcohol-induced liver injury in mice through inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Guizhou Medicine,2021 ,45 (5 ):675 −678 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-744X.2021.05.001[73] 曾瑜, 刘婧, 黄真真, 等. 姜黄素对急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠抗氧化功能的影响[J]. 卫生研究,2014,43(2):282−285. [ZENG Y, LIU J, HUANG Z Z, et al. Effects of curcumin on antioxidant function in mice with acute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Health Research,2014,43(2):282−285. ZENG Y, LIU J, HUANG Z Z, et al . Effects of curcumin on antioxidant function in mice with acute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Health Research,2014 ,43 (2 ):282 −285 .[74] 原海忠, 韩刚, 董月, 等. 姜黄素固体分散体对大鼠酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 现代预防医学,2009,36(17):3350−3352,3357. [YUAN H Z, HAN G, DONG Y, et al. Protective effect of curcumin solid dispersion on alcoholic liver injury in rats[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine,2009,36(17):3350−3352,3357. YUAN H Z, HAN G, DONG Y, et al . Protective effect of curcumin solid dispersion on alcoholic liver injury in rats[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine,2009 ,36 (17 ):3350 −3352,3357 .[75] 韩刚, 原海忠, 董月, 等. 姜黄素固体分散体对大鼠肝损伤的防治作用[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2009,11(3):200−202. [HAN G, YUAN H Z, DONG Y, et al. Preventive effect of curcumin solid dispersions on liver injury in rats[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Chinese Medicine,2009,11(3):200−202. HAN G, YUAN H Z, DONG Y, et al . Preventive effect of curcumin solid dispersions on liver injury in rats[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Chinese Medicine,2009 ,11 (3 ):200 −202 .[76] 韩刚, 姚国贤, 原海忠, 等. 姜黄素固体分散体对酒精性肝损伤大鼠氧化应激的影响[J]. 世界华人消化杂志,2009,17(5):500−503. [HAN G, YAO G X, YUAN H Z, et al. Effects of curcumin solid dispersion on oxidative stress in alcoholic liver-injured rats[J]. World Journal of Chinese Digestion,2009,17(5):500−503. doi: 10.11569/wcjd.v17.i5.500 HAN G, YAO G X, YUAN H Z, et al . Effects of curcumin solid dispersion on oxidative stress in alcoholic liver-injured rats[J]. World Journal of Chinese Digestion,2009 ,17 (5 ):500 −503 . doi: 10.11569/wcjd.v17.i5.500[77] 张德馨, 王淑华, 孙仟, 等. 山楂叶总黄酮提取工艺与药理作用研究进展[J]. 食品与药品,2021,23(4):380−385. [ZHANG D X, WANG S H, SUN Q, et al. Advances in the extraction process and pharmacological effects of total flavonoids from Hawthorn leaves[J]. Food and Drug,2021,23(4):380−385. ZHANG D X, WANG S H, SUN Q, et al . Advances in the extraction process and pharmacological effects of total flavonoids from Hawthorn leaves[J]. Food and Drug,2021 ,23 (4 ):380 −385 .[78] 李素婷, 陈龙, 王冉, 等. 山楂叶总黄酮对小鼠急性酒精性肝损伤保护作用的实验研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2012,23(11):2903−2904. [LI S T, CHEN L, WWANG R, et al. Experimental study on the protective effect of total flavonoids of Hawthorn leaves on acute alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Shizhen Chinese Medicine and Chinese Medicine,2012,23(11):2903−2904. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2012.11.109 LI S T, CHEN L, WWANG R, et al . Experimental study on the protective effect of total flavonoids of Hawthorn leaves on acute alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Shizhen Chinese Medicine and Chinese Medicine,2012 ,23 (11 ):2903 −2904 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2012.11.109[79] 李素婷, 张子俊, 杜超, 等. 山楂叶总黄酮对酒精性肝损伤小鼠脂质过氧化水平的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2014,34(4):1012−1014. [LI S T, ZHANG Z J, DU C, et al. Effects of total flavonoids of Hawthorn leaves on lipid peroxidation levels in alcoholic liver-injured mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology,2014,34(4):1012−1014. LI S T, ZHANG Z J, DU C, et al . Effects of total flavonoids of Hawthorn leaves on lipid peroxidation levels in alcoholic liver-injured mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology,2014 ,34 (4 ):1012 −1014 .[80] 李素婷, 王琳, 许倩, 等. 山楂叶总黄酮对急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠肝细胞凋亡及Bcl-2、Bax蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2016,36(14):3375−3377. [LI S T, WANG L, XU Q, et al. Effects of total flavonoids of Hawthorn leaves on apoptosis and expression of Bcl-2 and Bax proteins in hepatocytes of mice with acute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology,2016,36(14):3375−3377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2016.14.011 LI S T, WANG L, XU Q, et al . Effects of total flavonoids of Hawthorn leaves on apoptosis and expression of Bcl-2 and Bax proteins in hepatocytes of mice with acute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology,2016 ,36 (14 ):3375 −3377 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2016.14.011[81] 李素婷, 吴淑彦, 杜超, 等. 山楂叶总黄酮对酒精性肝损伤小鼠肝细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2015,35(7):1889−1891. [LI S T, WU S Y, DU C, et al. Effect of total flavonoids of Hawthorn leaves on apoptosis of hepatocytes in mice with alcoholic liver injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology,2015,35(7):1889−1891. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2015.07.072 LI S T, WU S Y, DU C, et al . Effect of total flavonoids of Hawthorn leaves on apoptosis of hepatocytes in mice with alcoholic liver injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology,2015 ,35 (7 ):1889 −1891 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2015.07.072[82] 常陆林. 山楂黄酮提取、纯化工艺及其对酒精性肝损伤影响的研究[D]. 郑州:郑州大学, 2010. [CHANG L L. Study on the extraction and purification process of Hawthorn flavonoids and its effect on alcoholic liver injury[D]. Zhengzhou:Zhengzhou University, 2010. CHANG L L. Study on the extraction and purification process of Hawthorn flavonoids and its effect on alcoholic liver injury[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2010.
[83] 潘莹, 江海燕, 丁国强. 大果山楂总黄酮对实验性酒精肝损伤保护作用的研究[J]. 中医药学刊,2004(12):2293−2311. [PAN Y, JIANG H Y, DING G Q. Study on the protective effect of total flavonoids of Hawthorn on experimental alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2004(12):2293−2311. PAN Y, JIANG H Y, DING G Q . Study on the protective effect of total flavonoids of Hawthorn on experimental alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2004 (12 ):2293 −2311 .[84] 魏蕾, 卫倩倩, 李思维, 等. 山楂酸对急性酒精肝损伤小鼠部分生化指标的影响[J]. 临床医学研究与实践,2020,5(33):4−6. [WEI L, WEI Q Q, LI S W, et al. Effects of hawthorn acid on some biochemical indicators in mice with acute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Clinical Medicine Research and Practice,2020,5(33):4−6. WEI L, WEI Q Q, LI S W, et al . Effects of hawthorn acid on some biochemical indicators in mice with acute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Clinical Medicine Research and Practice,2020 ,5 (33 ):4 −6 .[85] YAN S L, YANG H T, LEE H L, et al. Protective effects of maslinic acid against alcohol-induced acute liver injury in mice[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2014,74:149−155. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2014.09.018
[86] 叶丽云, 孟国良, 吴龙月, 等. 灵芝子实体多糖对小鼠急性酒精肝损伤预防的代谢组分析[J]. 菌物学报,2021,40(9):2376−2389. [YE L Y, MENG G L, WU L Y, et al. Metabolome analysis of Ganoderma lucidum fruiting body polysaccharides for the prevention of acute alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Mycosystema,2021,40(9):2376−2389. YE L Y, MENG G L, WU L Y, et al . Metabolome analysis of Ganoderma lucidum fruiting body polysaccharides for the prevention of acute alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Mycosystema,2021 ,40 (9 ):2376 −2389 .[87] 张若冰, 杨玉赫, 李陈雪, 等. 灵芝多糖药理作用及机制的研究进展[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2023,35(5):879−887. [ZHANG R B, YANG Y H, LI C X, et al. Research progress on pharmacological effects and mechanisms of G anoderma lucidum polysaccharides[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2023,35(5):879−887. ZHANG R B, YANG Y H, LI C X, et al . Research progress on pharmacological effects and mechanisms of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2023 ,35 (5 ):879 −887 .[88] 叶丽云, 程冰, 马水丽, 等. 赤芝多糖对小鼠急性酒精性肝损伤的保护效果和作用机制[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(5):103−110. [YE L Y, CHENG B, MA S L, et al. Protective effect and mechanism of erythroxyphy polysaccharides on acute alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Food Science,2022,43(5):103−110. YE L Y, CHENG B, MA S L, et al . Protective effect and mechanism of erythroxyphy polysaccharides on acute alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Food Science,2022 ,43 (5 ):103 −110 .[89] 赵婷婷, 戴映笛, 舒昉, 等. 灵芝菌丝体多糖提取工艺优化及其对慢性酒精肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(5):388−396. [ZHAO T T, DAI Y D, SHU F, et al. Optimization of Ganoderma lucidum mycelium polysaccharide extraction process and its protective effect on chronic alcoholic liver injury[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(5):388−396. ZHAO T T, DAI Y D, SHU F, et al . Optimization of Ganoderma lucidum mycelium polysaccharide extraction process and its protective effect on chronic alcoholic liver injury[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023 ,44 (5 ):388 −396 .[90] 魏晓霞. 灵芝三萜组分GLA的抗肿瘤及对急性肝损伤保护作用的研究[D]. 福州:福建医科大学, 2011. [WEI X X. Antitumor and protective effect of Ganoderma lucidum triterpene component GLA on acute liver injury[D]. Fuzhou:Fujian Medical University, 2011. WEI X X. Antitumor and protective effect of Ganoderma lucidum triterpene component GLA on acute liver injury[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Medical University, 2011.
[91] LÜ X C, WU Q, CAO Y J, et al. Ganoderic acid A from Ganoderma lucidum protects against alcoholic liver injury through ameliorating the lipid metabolism and modulating the intestinal microbial composition[J]. Food Function,2022,13(10):5820−5837. doi: 10.1039/D1FO03219D
[92] CAO Y J, HUANG Z R, YOU S Z, et. al. The protective effects of ganoderic acids from Ganoderma lucidum fruiting body on alcoholic liver injury and intestinal microflora disturbance in mice with excessive alcohol intake[J]. Foods,2022,11(7):949−956. doi: 10.3390/foods11070949
[93] 马丙钧. 灵芝酸A对急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠的保护作用及机制研究[D]. 郑州:郑州大学, 2019. [MA B J. Protective effect and mechanism of ganoderic acid A on mice with acute alcoholic liver injury[D]. Zhengzhou:Zhengzhou University, 2019. MA B J. Protective effect and mechanism of ganoderic acid A on mice with acute alcoholic liver injury[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2019.
[94] 李晓宇, 李晶, 王一博, 等. 人参皂苷对酒精性肝损伤的保护作用研究[J]. 药物评价研究,2015,38(5):512−515. [LI X Y, LI J, WANG Y B, et al. Protective effect of ginsenosides on alcoholic liver injury[J]. Pharmaceutical Evaluation Research,2015,38(5):512−515. LI X Y, LI J, WANG Y B, et al . Protective effect of ginsenosides on alcoholic liver injury[J]. Pharmaceutical Evaluation Research,2015 ,38 (5 ):512 −515 .[95] GAO Y, CHU S, LI J, et. al. Anti-inflammatory function of ginsenoside Rg1 on alcoholic hepatitis through glucocorticoid receptor related nuclear factor-kappa B pathway[J]. Ethnopharmacol,2015(173):231−240.
[96] 张宇, 王洪波, 朱振宇, 等. 人参皂苷CK抑制内质网应激防治酒精性肝损伤[J]. 安徽医科大学学报,2019,54(5):710−715. [ZHANG Y, WANG H B, ZHU Z Y, et al. Ginsenoside CK inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress for the prevention of alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Anhui Medical University,2019,54(5):710−715. ZHANG Y, WANG H B, ZHU Z Y, et al . Ginsenoside CK inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress for the prevention of alcoholic liver injury[J]. Journal of Anhui Medical University,2019 ,54 (5 ):710 −715 .[97] 李明珂, 陈徐佳, 武绍梅, 等. 人参皂苷Rh1、CK改善酒精性肝损伤及线粒体结构的研究[J]. 重庆医学,2018,47(31):3973−3977. [LI M K, CHEN X J, WU S M, et al. Study on the improvement of alcoholic liver injury and mitochondrial structure by ginsenosides Rh1 and CK[J]. Chongqing Medical Journal,2018,47(31):3973−3977. LI M K, CHEN X J, WU S M, et al . Study on the improvement of alcoholic liver injury and mitochondrial structure by ginsenosides Rh1 and CK[J]. Chongqing Medical Journal,2018 ,47 (31 ):3973 −3977 .[98] 尹春金. 人参皂苷Re对乙醇诱导的大鼠H4IIE肝细胞线粒体功能损伤的作用机制[D]. 延吉:延边大学, 2022. [YIN C J. Mechanism of Ginsenoside Re on Ethanol-induced mitochondrial damage in rat H4IIE hepatocytes[D]. Yanji:Yanbian University, 2022. YIN C J. Mechanism of Ginsenoside Re on Ethanol-induced mitochondrial damage in rat H4IIE hepatocytes[D]. Yanji: Yanbian University, 2022.
[99] GAO Y, CHU S F, XIA C Y, et. al. Rg1 Attenuates alcoholic hepatic damage through regulating AMP-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signal pathways[J]. Journal of Asian Natural Products Research,2016,18(8):765−778. doi: 10.1080/10286020.2016.1162787





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
